Systematic review of immunomodulatory therapies for hidradenitis suppurativa
- PMID: 31190730
- PMCID: PMC6526329
- DOI: 10.2147/BTT.S199862
Systematic review of immunomodulatory therapies for hidradenitis suppurativa
Abstract
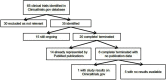
Background: Greater understanding of the roles of tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-1β, IL-10, and the IL-23/T-helper (Th) 17 and IL-12/Th1 pathways in immune dysregulation in moderate/severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) has helped in developing new regimens. We aim to review the use of different immunomodulatory therapies used to manage HS. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted on the PubMed and Clinicaltrials.gov databases from 1 January 1947 to 31 December 2018. Only clinical trials, case reports, case series and retrospective analyses published in the English language were included. Results: Our search yielded 107 articles and 35 clinical trials, of which 15 are still ongoing. The tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors adalimumab and infliximab were the most comprehensively studied agents. Published data from clinical trials support the efficacy of adalimumab, infliximab, anakinra, ustekinumab, bermekimab and apremilast but not etanercept and MEDI8968. Clinical trials for CJM112 have been completed, with results awaiting publication. Trials are underway for secukinumab, IFX-1, INCB054707 and bimekizumab. Biologics used in smaller cohorts include canakinumab, golimumab and rituximab. Most agents are well tolerated and demonstrate a good safety profile, with the most commonly reported adverse event being infections. Discussion and conclusions: To date, adalimumab is the only biologic which has been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration for HS. However, other agents also show promise, with further trials underway to evaluate their efficacy, tolerability and safety profiles. Different clinical measurement scores and endpoints used to make direct comparison difficult. Longitudinal surveillance and pooled registry data are paramount to evaluate the long-term safety profile and efficacy of therapy.
Keywords: Hidradenitis suppurativa; adalimumab; biologics; infliximab; secukinumab; tumor necrosis factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Hazel H Oon is a clinical investigator for Janssen, Novartis and Pfizer. She has also served as a speaker and advisory board member for AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis and Eli Lilly. Hazel H Oon reports grants and personal fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, and Pfizer outside the submitted work.The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biologics and Small Molecule Inhibitors for Treating Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 2;10(6):1303. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061303. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of biologics and JAK inhibitors in the management of moderate to severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa treatment: a scoping review.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 May 25;316(6):259. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03121-x. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38795234
-
New and Emerging Targeted Therapies for Hidradenitis Suppurativa.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 29;23(7):3753. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073753. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A safety review of biologic therapies for the management of hidradenitis suppurativa and unmet needs.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2021 Oct;20(10):1147-1161. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2021.1924147. Epub 2021 May 12. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2021. PMID: 33910441 Review.
-
Investigational drugs in clinical trials for Hidradenitis Suppurativa.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018 Jan;27(1):43-53. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1412430. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29188733 Review.
Cited by
-
Surgical Management of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Narrative Review.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Jan;15(1):35-41. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35309275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Interleukin-17A in the Pathomechanisms of Periodontitis and Related Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 17;13:862415. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.862415. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35371044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Implementation of Biologics and Small Molecules in the Treatment of Hidradenitis Suppurativa.Drugs. 2021 Aug;81(12):1397-1410. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01566-2. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34283386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Rare Inflammatory Kidney Diseases: Drugs Targeting the Terminal Complement Pathway.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 10;11:599417. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.599417. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33362783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Mechanisms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Inflammation and miRNA Insights.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 Dec 11;17:2829-2846. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S483871. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39677852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deckers IE, van der Zee HH, Prens EP. Epidemiology of hidradenitis suppurativa: prevalence, pathogenesis, and factors associated with the development of HS. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2014;3(1):54–60. doi:10.1007/s13671-013-0064-8 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources