Andrographolide attenuates bupivacaine-induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells through preserving Akt/mTOR activity
- PMID: 31190744
- PMCID: PMC6529178
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S201122
Andrographolide attenuates bupivacaine-induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells through preserving Akt/mTOR activity
Abstract
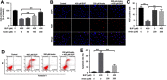
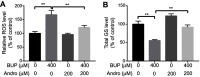
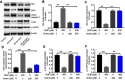
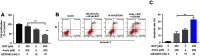
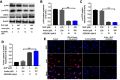
Background: Bupivacaine (Bup) is the most commonly used local anesthetic. However, Bup induces cytotoxicity, especially in older patients. Recent reports have indicated that andrographolide (Andro) exhibits protective effects on human neurons. Nevertheless, whether Andro can inhibit Bup-induced cytotoxicity remains unclear. As such, we investigated the effect of Andro on Bup-induced cytotoxicity of SH-SY5Y cells in the present study. Methods: Western blotting was used to examine expression of Bax, Bcl2, active caspase 3, p-Akt, and p-mTOR in SH-SY5Y cells. In addition, ELISA was used to detect levels of total glutathione and reactive oxygen species in cells. Results: We found that Andro attenuated Bup-induced cytotoxicity of SH-SY5Y cells. In addition, Andro inhibited Bup-induced apoptosis via downregulating the expression of Bax and active caspase 3 and upregulating the proteins Bcl2, p-Akt, and p-mTOR in SH-SY5Y cells. Moreover, Andro alleviated Bup-induced oxidative damage in SH-SY5Y cells via downregulating the level of reactive oxygen species and upregulating of the level of total glutathione. More significantly, inhibition of Akt abolished the protective effect of Andro in Bup-treated SH-SY5Y cells. Conclusion: Our findings indicated that Andro played a neuroprotective role via preserving Akt/mTOR activity and increasing antioxidative status in Bup-treated SH-SY5Y cells. Therefore, Andro may be a potential agent for the treatment of human cytotoxicity induced by Bup.
Keywords: Akt; andrographolide; apoptosis; bupivacaine; cytotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
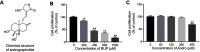
Similar articles
-
Bupivacaine Reduces the Viability of SH-SY5Y Cells and Promotes Apoptosis by the Inhibition of Akt Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2025 Apr 12;50(2):143. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04386-y. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40220051
-
Tetramethylpyrazine attenuated bupivacaine-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells through regulating apoptosis, autophagy and oxidative damage.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Apr 17;13:1187-1196. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S196172. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31114159 Free PMC article.
-
Isorhamnetin ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal damage via targeting FOSL1 to activate AKT/mTOR in 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cells.J Neurophysiol. 2025 Jan 1;133(1):22-33. doi: 10.1152/jn.00351.2024. Epub 2024 Nov 19. J Neurophysiol. 2025. PMID: 39560297
-
Capillarisin protects SH-SY5Y cells against bupivacaine-induced apoptosis via ROS-mediated PI3K/PKB pathway.Life Sci. 2020 Oct 15;259:118279. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118279. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32798562
-
Andrographolide: A promising therapeutic agent against organ fibrosis.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Dec 15;280:116992. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116992. Epub 2024 Oct 20. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39454221 Review.
Cited by
-
Bupivacaine Reduces the Viability of SH-SY5Y Cells and Promotes Apoptosis by the Inhibition of Akt Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2025 Apr 12;50(2):143. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04386-y. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40220051
-
Urolithin A attenuates bupivacaine-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells by regulating the SIRT1-activated PI3K/AKT pathway.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Nov;39(11):1485-1492. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-737. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 38587058
-
Effect of species, concentration and volume of local anesthetics on intervertebral disk degeneration in rats with discoblock.Eur Spine J. 2022 Nov;31(11):2960-2971. doi: 10.1007/s00586-022-07398-2. Epub 2022 Sep 24. Eur Spine J. 2022. PMID: 36152221
-
Development of Potential Antitumor Agents from the Scaffolds of Plant-Derived Terpenoid Lactones.J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 24;63(24):15410-15448. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01449. Epub 2020 Dec 8. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33289552 Free PMC article.
-
Andrographolide contributes to spinal cord injury repair via inhibition of apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 7;13:949502. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.949502. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36278181 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

