Bioequivalence of paclitaxel protein-bound particles in patients with breast cancer: determining total and unbound paclitaxel in plasma by rapid equilibrium dialysis and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 31190752
- PMCID: PMC6535670
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S200679
Bioequivalence of paclitaxel protein-bound particles in patients with breast cancer: determining total and unbound paclitaxel in plasma by rapid equilibrium dialysis and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
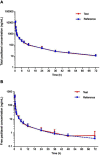
Background and objective: Paclitaxel protein-bound particles for injectable suspension (nab-paclitaxel) showed many advantages in safety, effectiveness, and convenience. Different from conventional formulations, the bioequivalence evaluation of nab-paclitaxel formulations requires to determine the total amount of paclitaxel in plasma and the unbound paclitaxel to reflect their in vivo disposition. This study aimed to develop an analytical method to quantify the total and unbound paclitaxel in plasma and evaluate the bioequivalence of two formulations of nab-paclitaxel in patients with breast cancer. Materials and methods: An open-label, randomized, two-period crossover study was completed among 24 Chinese patients with breast cancer. The patients were randomized to receive either the test formulation on cycle 1 day 1 and after 21 days in cycle 2 day 1 by the reference formulation (Abraxane®), or vice versa. Rapid equilibrium dialysis was adopted to separate the unbound paclitaxel in human plasma. Total and unbound paclitaxel concentrations were measured by the validated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry methods over the range of 5.00-15,000 and 0.200-200 ng/mL, respectively. The bioequivalence of the test formulation to the reference formulation was assessed using the Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency guidelines. Results: All the 90% confidence intervals (CIs) of the geometric mean ratios fell within the predetermined acceptance range. The 90% CIs for the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) from 0 h to 72 h (AUC0-t), AUC from time zero to infinity (AUC0-∞), and peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) for total paclitaxel were 92.03%-98.05%, 91.98%-99.37%, and 91.37%-99.36%, respectively. The 90% CIs of AUC0-t, AUC0-∞, and Cmax for unbound paclitaxel were 86.77%-97.88%, 86.81%-97.88%, and 87.70%-98.86%, respectively. Conclusion: Bioequivalence between the two nab-paclitaxel formulations was confirmed for total and unbound paclitaxel at the studied dose regimen.
Keywords: bioequivalence; nab-paclitaxel; pharmacokinetics; rapid equilibrium dialysis; unbound fraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Adams JD, Flora KP, Goldspiel BR, et al. Taxol: a history of pharmaceutical development and current pharmaceutical concerns. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1993;(15):141–147. - PubMed
-
- Rowinsky EK, Cazenave LA, Donehower RC. Taxol: a novel investigational antimicrotubule agent. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990;82(15):1247–1259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical