Reticulocyte levels have an ambivalent association with hypertension and atherosclerosis in the elderly: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 31190771
- PMCID: PMC6512840
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S197982
Reticulocyte levels have an ambivalent association with hypertension and atherosclerosis in the elderly: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
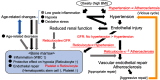
Purpose: Age-related reduction in bone marrow activity has been shown to cause anemia, and hypertension and endothelial dysfunction (atherosclerosis) are age-related diseases. However, recent studies have revealed a close association between bone marrow activity and endothelial maintenance. This study aimed to determine the association between elevated reticulocyte levels in conjunction with vigorous bone marrow activity and hypertension and atherosclerosis among the elderly. Study population and Methods: To determine the associations between reticulocyte levels and hypertension and atherosclerosis, we conducted a cross-sectional study of 2,098 elderly Japanese individuals, aged between 60 and 89 years, who had participated in an annual health check-up in 2014. Results: Of the total study population, 1,348 individuals were diagnosed with hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg and/or having used antihypertensive medication), and 393 were diagnosed with atherosclerosis (carotid intima-media thickness ≥1.1 mm). Reticulocyte levels were found to be significantly positively associated with hypertension and inversely associated with atherosclerosis. Cardiovascular risk factor-adjusted odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals for hypertension and atherosclerosis, when raised incrementally by 1 standard deviation to determine reticulocyte levels (5.5×104 cells/μL for men and 5.0×104 cells/μL for women), were 1.12 (1.01, 1.25) and 0.83 (0.72, 0.94), respectively. Conclusion: Along with established cardiovascular risk factors, reticulocyte levels in elderly Japanese individuals were found to be positively associated with hypertension and inversely associated with atherosclerosis. This finding may help clarify the background mechanisms concerning the association between bone marrow activity and vascular remodeling.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; hypertension; reticulocyte.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Shi Q, Rafii S, Wu MH, et al. Evidence for circulating bone marrow-derived endothelial cells. Blood. 1998;92:362–367. - PubMed
-
- Brusnahan SK, McGuire TR, Jackson JD, et al. Human blood and marrow side population stem cell and Stro-1 positive bone marrow stromal cell numbers decline with age, with an increase in quality of surviving stem cells: correlation with cytokines. Mech Ageing Dev. 2010;131:718–722. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2010.10.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

