Controlled drug delivery systems for cancer based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles
- PMID: 31190798
- PMCID: PMC6512630
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S198848
Controlled drug delivery systems for cancer based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles
Abstract
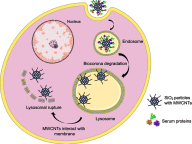
The implementation of nanotechnology in medicine has opened new research horizons particularly in the field of therapeutic delivery. Mesoporous silica particles have emerged as biocompatible drug delivery systems with an enormous potential in the treatment of cancer among many other pathologies. In this review, we focus on the unique properties of these particles as chemotherapy delivery carriers. Here, we summarize the general characteristics of these nanomaterials - including their physicochemical properties and customizable surfaces - different stimuli that can be used to trigger targeted drug release, biocompatibility and finally, the drawbacks of these types of nanomaterials, highlighting some of the most important features of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery.
Keywords: biocompatibility; biodegradability; drug release; nanocarrier; targeted drug delivery; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Chemoresponsive smart mesoporous silica systems - An emerging paradigm for cancer therapy.Int J Pharm. 2018 Dec 20;553(1-2):310-326. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.10.026. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Int J Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30316004 Review.
-
Silica materials in drug delivery applications.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2011 Sep;8(3):269-76. doi: 10.2174/157016311796799026. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2011. PMID: 21291408 Review.
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular controlled drug delivery.Small. 2010 Sep 20;6(18):1952-67. doi: 10.1002/smll.200901789. Small. 2010. PMID: 20690133 Review.
-
Aerosol-Assisted Synthesis of Tailor-Made Hollow Mesoporous Silica Microspheres for Controlled Release of Antibacterial and Anticancer Agents.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Feb 12;12(6):6885-6898. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b20510. Epub 2020 Jan 31. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 31967774
-
Cell microenvironment stimuli-responsive controlled-release delivery systems based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles.J Food Drug Anal. 2014 Mar;22(1):18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Feb 1. J Food Drug Anal. 2014. PMID: 24673901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design of Polymeric and Biocompatible Delivery Systems by Dissolving Mesoporous Silica Templates.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 16;21(24):9573. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249573. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33339139 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterial-mediated autophagy: coexisting hazard and health benefits in biomedicine.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2020 Oct 16;17(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12989-020-00372-0. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 33066795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Applications of the CRISPR-Cas System.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Sep 15;9(9):477. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9090477. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36135023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solid Lipid Particles for Lung Metastasis Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jan 13;13(1):93. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13010093. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33451053 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Ordered Porous Silica Materials in Drug Delivery: A Review.Molecules. 2024 Dec 3;29(23):5713. doi: 10.3390/molecules29235713. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39683872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

