The functions of microRNA-124 on bladder cancer
- PMID: 31190856
- PMCID: PMC6511623
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S193661
The functions of microRNA-124 on bladder cancer
Abstract
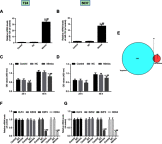
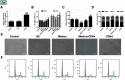
Background: To detect the expression of miR-124 in bladder cancer (BC) cell lines and tissue specimens and to analyze its association with the growth of the BC cells. Methods: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was applied to examine the expression of miR-124 in BC cell lines and tissues. The function of miR-124 in modulating cell proliferation was assessed in BC cells with miRNA-124 overexpression; the cell viability was identified by Cell Count Kit-8; flow cytometry was employed to detect the cell cycle; the expressions of E2F3, cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), Ki-67 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were tested by qPCR and Western blot; angiogenesis experiment was performed to analysis changes in angiogenesis rate; and bioinformatics prediction and dual luciferase reporter system were employed to identify the target of miR-124. Results: Survival curve data showed that the expression of MicroRNA-124 was positively correlated with survival. MicroRNA-124 expression was significantly decreased in BC cell lines and tissues. Bioinformatics prediction and dual luciferase reporter system verified CDK4 as a direct target of miR-124, which regulated the proliferation of BC cells by directly inhibiting CDK4. BC cells over-expressing miR-124 showed significantly inhibited cell viability, decreased angiogenesis rate, prevented cell proliferation and diminished the expression of E2F3, CDK4, Ki-67 and VEGF. All of these changes were reversed by over-expressing CDK4. Conclusion: MicroRNA-124 suppressed the proliferation of CRC cells by directly targeting CDK4, which provides a target for improving the therapeutic effect of BC.
Keywords: CDK4; VEGF; bladder cancer; miR-124; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

