Identification of novel biomarkers and candidate small molecule drugs in non-small-cell lung cancer by integrated microarray analysis
- PMID: 31190860
- PMCID: PMC6526173
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S198621
Identification of novel biomarkers and candidate small molecule drugs in non-small-cell lung cancer by integrated microarray analysis
Abstract
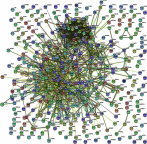
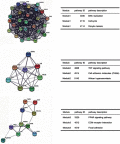
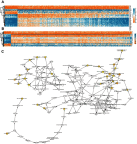
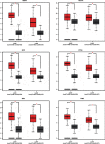
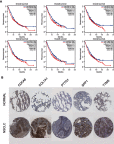
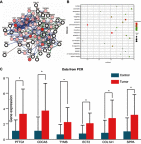
Background: Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains the leading cause of cancer morbidity and mortality worldwide. In the present study, we identified novel biomarkers associated with the pathogenesis of NSCLC aiming to provide new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for NSCLC. Methods: The microarray datasets of GSE18842, GSE30219, GSE31210, GSE32863 and GSE40791 from Gene Expression Omnibus database were downloaded. The differential expressed genes (DEGs) between NSCLC and normal samples were identified by limma package. The construction of protein-protein interaction (PPI) network, module analysis and enrichment analysis were performed using bioinformatics tools. The expression and prognostic values of hub genes were validated by GEPIA database and real-time quantitative PCR. Based on these DEGs, the candidate small molecules for NSCLC were identified by the CMap database. Results: A total of 408 overlapping DEGs including 109 up-regulated and 296 down-regulated genes were identified; 300 nodes and 1283 interactions were obtained from the PPI network. The most significant biological process and pathway enrichment of DEGs were response to wounding and cell adhesion molecules, respectively. Six DEGs (PTTG1, TYMS, ECT2, COL1A1, SPP1 and CDCA5) which significantly up-regulated in NSCLC tissues, were selected as hub genes according to the results of module analysis. The GEPIA database further confirmed that patients with higher expression levels of these hub genes experienced a shorter overall survival. Additionally, CMap predicted the 20 most significant small molecules as potential therapeutic drugs for NSCLC. DL-thiorphan was the most promising small molecule to reverse the NSCLC gene expression. Conclusions: Based on the gene expression profiles of 696 NSCLC samples and 237 normal samples, we first revealed that PTTG1, TYMS, ECT2, COL1A1, SPP1 and CDCA5 could act as the promising novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets for NSCLC. Our work will contribute to clarifying the molecular mechanisms of NSCLC initiation and progression.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis; candidate small molecules; non-small-cell lung cancer; novel biomarkers; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

