The reversal of MRP1 expression induced by low-frequency and low-intensity ultrasound and curcumin mediated by VEGF in brain glioma
- PMID: 31190861
- PMCID: PMC6526172
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S195205
The reversal of MRP1 expression induced by low-frequency and low-intensity ultrasound and curcumin mediated by VEGF in brain glioma
Abstract
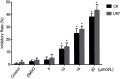
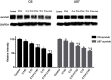
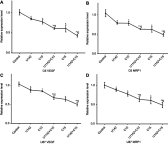
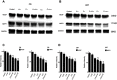
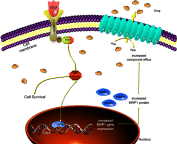
Purpose: To explore the effect of curcumin and low-frequency and low-intensity ultrasound (LFLIU) on C6 and U87 cell, and whether LFLIU could inhibit multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) by increasing the sensitivity of curcumin via vascular epithelial growth factor (VEGF)/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway targeting. Methods: C6 and U87 cells were treated with various doses of curcumin and/or different intensities of LFLIU for 60 s. After 24 hrs, the effects of curcumin and/or LFLIU on the proliferation of C6 and U87 cells were examined. Real-time PCR and western blot analysis were used to detect the expression of VEGF and MRP1 at both mRNA and protein levels. The expression of MRP1 in C6 and U87 cells was also determined following stimulation with recombinant human VEGF and/or LY294002. Results: Curcumin and LFLIU inhibited the proliferation of glioma cells in an intensity- or dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, survivin was significant after combined treatment compares with that of curcumin or LFLIU treatment alone. VEGF and MRP1 were highly expressed in C6 and U87 cells, curcumin and LFLIU alone or in combination could decrease the expression of both VEGF and MRP1. MRP1 expression was down-regulated following LY294002 treatment, which blocked after exposure to VEGF. Conclusion: The synergistic effects, such as a higher inhibition rate, and lower expressions of MRP1 and VEGF, of combined curcumin and LFLIU against glioma was much better than that of a single treatment. The down-regulation of MRP1 may be related with the VEGF/PI3K/Akt pathway in glioma.
Keywords: LFLIU; MRP1; VEGF; curcumin; glioma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

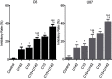

References
-
- Lamszus K, Ulbricht U, Matschke J, et al. Levels of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 1 in astrocytic tumors and its relation to malignancy, vascularity, and VEGF-A. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(4):1399–1405. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

