Curcumin reverses oxaliplatin resistance in human colorectal cancer via regulation of TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 31190888
- PMCID: PMC6529728
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S199601
Curcumin reverses oxaliplatin resistance in human colorectal cancer via regulation of TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway
Abstract
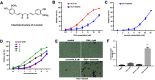
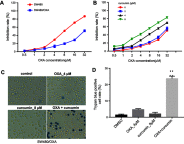
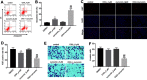
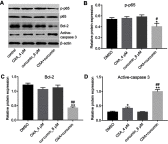
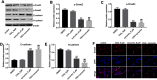
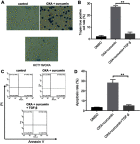
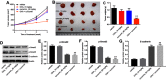
Background: Oxaliplatin (OXA) resistance is a main obstacle to the chemotherapy of colorectal cancer (CRC). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is mainly regulated by TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway, has gradually been recognized as an important mechanism for tumor chemoresistance. Studies have shown that curcumin regulated EMT processes in many human cancers. However, whether curcumin could regulate OXA resistance in CRC through modulating TGF-β/Smad signaling-mediated EMT remains unclear. Methods: In an attempt to investigate the effect of curcumin on OXA resistance in CRC, OXA-resistant cell line HCT116/OXA was established firstly. The effect of curcumin on cell proliferation was evaluated by MTT assay and Ki67 immunofluorescence staining, respectively. Cell apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry. In addition, transwell assay was used to detect the effect of curcumin on cell invasion and the activation of TGF-β/Smad signaling was examined by immunofluorescence and Western blot. Moreover, the therapeutic potential of curcumin was further examined in vivo using a CRC animal model. Results: The OXA-resistant cell line HCT116/OXA was successfully established, and combination of OXA with curcumin reduced OXA resistance in vitro. Besides, the combination treatment inhibited the expressions of p-p65 and Bcl-2, but increased the level of active-caspase3. In addition, curcumin inhibited EMT via regulation of TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway. Moreover, in vivo study confirmed curcumin could reverse OXA resistance in CRC. Conclusion: Our study indicated that curcumin could reserve OXA resistance in CRC through dampening TGF-β/Smads signaling in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway; colorectal cancer; curcumin; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; oxaliplatin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Petrelli F, Coinu A, Ghilardi M, Cabiddu M, Zaniboni A, Barni S. Efficacy of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy + bevacizumab as first-line treatment for advanced colorectal cancer: a systematic review and pooled analysis of published trials. Am J Clin Oncol. 2015;38(2):227–233. doi:10.1097/COC.0b013e3182a2d7b8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kopetz S, Hoff PM, Morris JS, et al. Phase II trial of infusional fluorouracil, irinotecan, and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer: efficacy and circulating angiogenic biomarkers associated with therapeutic resistance. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(3):453–459. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.24.8252 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

