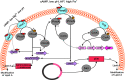
Molecular mechanisms related to colistin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae
- PMID: 31190901
- PMCID: PMC6519339
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S199844
Molecular mechanisms related to colistin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae
Abstract
Colistin is an effective antibiotic for treatment of most multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. It is used currently as a last-line drug for infections due to severe Gram-negative bacteria followed by an increase in resistance among Gram-negative bacteria. Colistin resistance is considered a serious problem, due to a lack of alternative antibiotics. Some bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, Enterobacteriaceae members, such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., and Klebsiella spp. have an acquired resistance against colistin. However, other bacteria, including Serratia spp., Proteus spp. and Burkholderia spp. are naturally resistant to this antibiotic. In addition, clinicians should be alert to the possibility of colistin resistance among multidrug-resistant bacteria and development through mutation or adaptation mechanisms. Rapidly emerging bacterial resistance has made it harder for us to rely completely on the discovery of new antibiotics; therefore, we need to have logical approaches to use old antibiotics, such as colistin. This review presents current knowledge about the different mechanisms of colistin resistance.
Keywords: Enterobacteriaceae; colistin; lipid A; mcr genes; two-component system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Health UDo, Control HSJCfD. Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. 2013;2013.
-
- Tenover FC, McGowan JE Jr. Reasons for the emergence of antibiotic resistance. Am J Med Sci. 1996;311(1):9–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous