Clinical evidence on the efficacy and tolerability of a topical medical device containing benzoylperoxide 4%, retinol 0.5%, mandelic acid 1% and lactobionic acid 1% in the treatment of mild facial acne: an open label pilot study
- PMID: 31190944
- PMCID: PMC6526677
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S182317
Clinical evidence on the efficacy and tolerability of a topical medical device containing benzoylperoxide 4%, retinol 0.5%, mandelic acid 1% and lactobionic acid 1% in the treatment of mild facial acne: an open label pilot study
Abstract
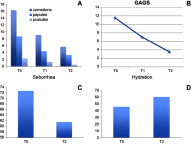
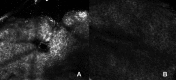
Background: Acne is a debilitating disorder that requires proper treatment depending on the clinical manifestations and pathogenetic factors, among which hyper-keratinization, seborrhea and bacterial proliferation. Combining active ingredients targeting the different mediators of acne pathogenesis may yield optimal outcomes. Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical effectiveness, safety and tolerability of a new topical medical device in cream containing benzoylperoxide 4%, pure retinol 0.05%, palmitate retinol 0.5%, mandelic acid 1% and glycyrrhetic acid on patients with mild acne. Patients and methods: Twenty consecutive patients of both sexes with mild acne were included in the study. The topical treatment was self-applied twice a day for 12 weeks. Evaluations included: Global Acne Grading System (GAGS); inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions count; reflectance confocal microscopy; seborrhea and hydration degree; photographic documentation; a questionnaire to assess tolerability. Results: The GAGS score showed a 39% reduction from T0 to T1 and 69.20% from T0 to T2. The count of comedonic lesions showed a 44% reduction from T0 to T1 and 65% from T0 to T2. The count of papular lesions diminished by 49.4% from T0 to T1 and by 62% from T0 to T2. The count of pustular lesions decreased by 43% from T0 to T1 and by 80% from T0 to T2. Improvement of hydration and a decrease of seborrhea degree were even observed. These clinical results were confirmed by reflectance confocal microscopy exam. Conclusion: The topical medical device has shown to be clinically effective and well tolerated for the treatment of mild acne. Side effects were mild, transient and well tolerated. The results of our study demonstrated a high tolerability of this new combination of benzoylperoxide 4% and retinol. Furthermore, our results suggested that the studied compound could be considered as a "maintenance treatment" after specific pharmacological treatment, even in more severe types of acne.
Keywords: acne vulgaris; alpha hydroxide acid; benzoyl peroxide; therapeutics; vitamin A.
Conflict of interest statement
This is a sponsor free trial. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
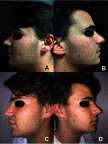
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

