Pain reduction and improved vascular health associated with daily consumption of an anti-inflammatory dietary supplement blend
- PMID: 31190960
- PMCID: PMC6526776
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S189064
Pain reduction and improved vascular health associated with daily consumption of an anti-inflammatory dietary supplement blend
Abstract
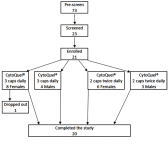
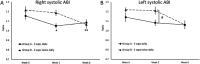
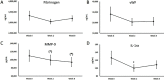
Purpose: The objective for this clinical pilot study was to evaluate changes to chronic pain, vascular health, and inflammatory markers when consuming a dietary supplement blend (DSB, CytoQuel®), containing curcumin, resveratrol, tocotrienols, N-Acetylcysteine, and epigallocatechin gallate. Materials and methods: An open-label study design was used where 21 study participants were evaluated at baseline and at 2 and 8 weeks after consuming DSB. Participants were randomized to consume 3 capsules once daily versus 2 capsules twice daily. Pain and activities of daily living questionnaires were used to gather subjective data on pain levels and interference with daily living. Blood pressure was measured in both arms and ankles, and the ankle-brachial index (ABI) calculated. Blood samples were used to evaluate markers associated with inflammation and cardiovascular health. Results: Highly significant reduction of chronic pain was seen after 8 weeks (p<0.01), both at rest and when physically active. Faster improvement was seen when consuming 3 capsules once daily, compared to 2 capsules twice daily. The pain reduction resulted in improved sleep quality (p<0.1), and improved social functioning (p<0.01), and less need for support from others (p<0.05), Normalization of mildly elevated ABI at study start was seen after 2 weeks. Plasma fibrinogen and von Willebrand Factor and serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) showed reduction after 2 weeks (not significant), whereas a reduction in serum interleukin-1 receptor antagonist-a (IL-1ra) was statistically significant after 2 weeks (p<0.05). Correlation between pain reduction and changes to MMP-9 after 8 weeks was highly significant (P<0.01), whereas correlation between pain reduction and changes to IL-1ra reached significance at 2 weeks for the group consuming 3 caps once daily (p<0.04). Conclusion: Consuming DSB helped manage pain, increased comfort during daily activities, and improved vascular function. This was associated with selective effects on specific blood biomarkers associated with inflammation and vascular health.
Keywords: ankle-brachial index; cardiovascular disease; fibrinogen; interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; matrix metalloproteinase-9; von Willebrand factor.
Conflict of interest statement
DEH is employed as the Director of Physician Education and Clinical Trials for the study sponsor, Research Nutritionals, LLC. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved Joint Mobility Associated with Reduced Inflammation Related to Consumption of Nopal Cactus Fruit Juice: Results from a Placebo-Controlled Trial Using Digital Inclinometry to Objectively Document Mobility of All Major Joints.Clin Interv Aging. 2020 Dec 9;15:2341-2352. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S267451. eCollection 2020. Clin Interv Aging. 2020. PMID: 33328728 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A novel, multi-ingredient supplement to manage elevated blood lipids in patients with no evidence of cardiovascular disease: a pilot study.Altern Ther Health Med. 2014 Sep-Oct;20(5):18-23. Altern Ther Health Med. 2014. PMID: 25141367 Clinical Trial.
-
Results of blood inflammatory markers are associated more strongly with toe-brachial index than with ankle-brachial index in patients with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2004 Jun;27(6):1381-6. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.6.1381. Diabetes Care. 2004. PMID: 15161792
-
Tiotropium bromide. A review of its use as maintenance therapy in patients with COPD.Treat Respir Med. 2004;3(4):247-68. doi: 10.2165/00151829-200403040-00005. Treat Respir Med. 2004. PMID: 15350163 Review.
-
Novel Augmentation Strategies in Major Depression.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5338. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385173 Review.
Cited by
-
Improved Joint Mobility Associated with Reduced Inflammation Related to Consumption of Nopal Cactus Fruit Juice: Results from a Placebo-Controlled Trial Using Digital Inclinometry to Objectively Document Mobility of All Major Joints.Clin Interv Aging. 2020 Dec 9;15:2341-2352. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S267451. eCollection 2020. Clin Interv Aging. 2020. PMID: 33328728 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Commentary on "Pain Reduction and Improved Vascular Health Associated with Daily Consumption of an Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Supplement Blend" [Response to Letter].J Pain Res. 2025 Jan 11;18:159-160. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S510281. eCollection 2025. J Pain Res. 2025. PMID: 39816203 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Role of Tocotrienol in Arthritis Management-A Scoping Review of Literature.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 2;16(3):385. doi: 10.3390/ph16030385. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36986484 Free PMC article.
-
A Commentary on "Pain Reduction and Improved Vascular Health Associated with Daily Consumption of an Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Supplement Blend" [Letter].J Pain Res. 2024 Dec 10;17:4197-4198. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S507795. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39679429 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

