Apolipoprotein M could inhibit growth and metastasis of SMMC7721 cells via vitamin D receptor signaling
- PMID: 31190977
- PMCID: PMC6525829
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S202799
Apolipoprotein M could inhibit growth and metastasis of SMMC7721 cells via vitamin D receptor signaling
Abstract
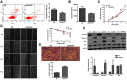
Objective: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors with high mortality-to-incidence ratios. Apolipoprotein M (ApoM), a member of the apolipoprotein family, is mainly synthesized in the liver, whereas its role in HCC has not been elucidated. Here, we examined the effect of ApoM on the biological behavior of HCC cells and the possible mechanisms. Methods: We used CRISPR/Cas9 technology to knock out ApoM in SMMC7721 cells. Differentially expressed genes before and after ApoM knockout (KO) were analyzed by GeneChip microarrays and confirmed by qRT-PCR. Cell assays of proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion were performed in SMMC7721 cells, and the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers was performed by western blot. And we performed functional recovery experiments by overexpressing vitamin D receptor (VDR) in SMMC7721. Results: The ApoM-KO SMMC7721 cell line was successfully constructed using the CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Our results showed that silencing ApoM suppressed apoptosis and promoted proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT of SMMC7721 cells. The microarray data revealed that a total of 1,868 differentially expressed genes were identified, including VDR. The qRT-PCR and western blot verification results demonstrated that knocking out ApoM could significantly reduce the expression of VDR. The functional recovery experiments indicated that VDR overexpression could offset the inhibition of cell apoptosis and the promotion of cell proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT caused by knocking out ApoM in SMMC7721 cells. Conclusion: ApoM could function as a tumor suppressor to inhibit the growth and metastasis of SMMC7721 cells via VDR signaling in HCC.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; GeneChip microarrays; apolipoprotein M; hepatocellular carcinoma cells; vitamin D receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein M promotes growth and inhibits apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells through upregulation of ribosomal protein S27a.EXCLI J. 2021 Jan 21;20:145-159. doi: 10.17179/excli2020-2867. eCollection 2021. EXCLI J. 2021. PMID: 33564284 Free PMC article.
-
The miR-573/apoM/Bcl2A1-dependent signal transduction pathway is essential for hepatocyte apoptosis and hepatocarcinogenesis.Apoptosis. 2015 Oct;20(10):1321-37. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1153-x. Apoptosis. 2015. PMID: 26201458
-
Apolipoprotein M increases the expression of vitamin D receptor mRNA in colorectal cancer cells detected with duplex fluorescence reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Aug;16(2):1167-1172. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6716. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 29067439 Free PMC article.
-
ApoM suppresses kidney renal clear cell carcinoma growth and metastasis via the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023 Jul 15;743:109642. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2023.109642. Epub 2023 May 19. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37211224
-
Effect of GnT-V knockdown on the proliferation, migration and invasion of the SMMC7721/R human hepatocellular carcinoma drug-resistant cell line.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jan;13(1):469-76. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4492. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26531171
Cited by
-
Apolipoprotein: prospective biomarkers in digestive tract cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 May;9(5):3712-3720. doi: 10.21037/tcr-19-2106. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein M inhibits proliferation and migration of larynx carcinoma cells.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 10;10(1):19424. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76480-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33173129 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein M promotes growth and inhibits apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells through upregulation of ribosomal protein S27a.EXCLI J. 2021 Jan 21;20:145-159. doi: 10.17179/excli2020-2867. eCollection 2021. EXCLI J. 2021. PMID: 33564284 Free PMC article.
-
APOM Modulates the Glycolysis Process in Liver Cancer Cells by Controlling the Expression and Activity of HK2 via the Notch Pathway.Biochem Genet. 2025 Jan 4. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-11013-y. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 39754657
-
Vitamin D promotes the cisplatin sensitivity of oral squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting LCN2-modulated NF-κB pathway activation through RPS3.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Dec 9;10(12):936. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2177-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31819048 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

