Circulating microRNA as diagnostic biomarkers for haematological cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31190996
- PMCID: PMC6520596
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S199126
Circulating microRNA as diagnostic biomarkers for haematological cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
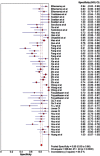
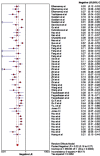
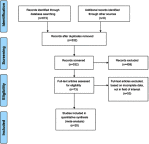
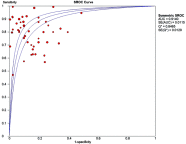
Purpose: Recent studies have validated microRNAs (miRNAs) as a diagnostic biomarker for haematological cancers. This study aimed to estimate the overall diagnostic accuracy of circulating miRNAs in haematological malignancies. Materials and Methods: Multiple databases (Google Scholar, PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library,) were searched until 19th August 2017. Results: The meta-analysis included 50 studies from 20 publications. The diagnostic accuracy was assessed by pooled specificity, sensitivity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) and area under the curve area (AUC) by random effect model. We used QUADAS (Quality Assessment for diagnostic accuracy studies) to evaluate the quality of the included studies. To perform the meta-analysis, we used Meta-Disk 1.4, Revman 5.3 and Stata 12.0 software. High diagnostic accuracy was demonstrated, with a sensitivity of 0.81, a specificity of 0.85, a PLR of 5.28, an NLR of 0.22, a DOR of 30.39, and an AUC of 0.91. Subgroup analyses showed better outcomes for the African population, combined miRNAs and leukaemia patients compared with other subgroups. Conclusion: Our results indicated that circulating miRNAs especially combined miRNA can be used as a diagnostic marker in haematological cancers.
Keywords: Specificity; diagnostic biomarkers; haematological cancers; miRNA; sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blood-Based Circulating MicroRNAs are Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Leukemia: Result from a Meta-Analysis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(3):939-49. doi: 10.1159/000443046. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26938054
-
Circulating microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for melanoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 May 8;23(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10891-6. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37158840 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA panels as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 7;9:915226. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.915226. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36419785 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating MicroRNA as Potential Source for Neurodegenerative Diseases Biomarkers.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;52(3):1494-1503. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8944-x. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25367880 Review.
-
The potential of circulating microRNAs as novel diagnostic biomarkers of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 19;24(1):1011. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09915-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39300343 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Noncoding RNAs in Extracellular Fluids as Cancer Biomarkers: The New Frontier of Liquid Biopsies.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 14;11(8):1170. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081170. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31416190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Contribution of MicroRNAs to the Inflammatory and Neoplastic Characteristics of Erdheim-Chester Disease.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 3;12(11):3240. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113240. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33153128 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Micro-Ribonucleic Acid Biomarkers for Early Detection of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Associated Complications-A Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 17;26(2):753. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020753. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Diagnostic Value of MicroRNAs as a Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Nov 29;2019:5179048. doi: 10.1155/2019/5179048. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31871941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Technologies for RNA-Directed Liquid Diagnostics.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 10;13(20):5060. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205060. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Slater DN. The new World Health Organization classification of haematopoietic and lymphoid tumours: A dermatopathological perspective. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:633–639. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

