Tissue-specific and exosomal miRNAs in lung cancer radiotherapy: from regulatory mechanisms to clinical implications
- PMID: 31191004
- PMCID: PMC6525830
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S198966
Tissue-specific and exosomal miRNAs in lung cancer radiotherapy: from regulatory mechanisms to clinical implications
Abstract
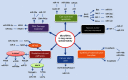
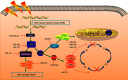
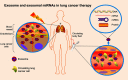
Lung cancer is the most prevalent and deadly malignancy. Radiotherapy is a major treatment modality for lung cancer. Nevertheless, radioresistance poses a daunting challenge that largely limits the efficacy of radiotherapy. There is a pressing need for deciphering molecular mechanisms underlying radioresistance and elucidating novel therapeutic targets for individualized radiotherapy. MicroRNAs are categorized as small noncoding RNAs that modulate target-gene expression posttranscriptionally and are implicated in carcinogenesis and cancer resistance to treatment. Overwhelming evidence has unraveled that tissue-specific miRNAs are essential for regulation of the radiosensitivity in lung cancer cells through a complex interaction with multiple biological processes and radiation-induced pathways. Moreover, exosome-derived miRNAs are a novel horizon in lung cancer treatment in which exosomal miRNAs act as potential diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers of radiotherapy. In the present review, we discuss the mediation of key biological processes and signaling pathways by tissue-specific miRNAs in lung cancer radiotherapy. Additionally, we provide new insight into the potential significance of exosomal miRNAs in radiation response. Lastly, we highlight miRNAs as promising predictors and therapeutic targets to tailor personalized lung cancer radiotherapy.
Keywords: exosome; lung cancer; microRNAs; personalized radiotherapy; radioresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting MicroRNAs in Prostate Cancer Radiotherapy.Theranostics. 2017 Jul 23;7(13):3243-3259. doi: 10.7150/thno.19934. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 28900507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of miRNAs affects radiobiological response of lung cancer stem cells.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:851841. doi: 10.1155/2015/851841. Epub 2015 Mar 1. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25815339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of microRNA-1323 restores sensitivity to radiation by suppression of PRKDC activity in radiation-resistant lung cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2015 Jun;33(6):2821-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3884. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25823795
-
Radiation-induced miR-208a increases the proliferation and radioresistance by targeting p21 in human lung cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 12;35:7. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0285-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26754670 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma miRNAs in predicting radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):11927-11936. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5052-8. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27075472 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulations of miR-183-5p and Snail-Mediated Shikonin-Reduced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cervical Cancer Cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Feb 11;14:577-589. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S236216. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32103900 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle- and Mitochondria-Based Targeting of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Response to Radiation: Challenges and Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 15;16(12):2235. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122235. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-410 induces both epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radioresistance through activation of the PI3K/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jun 12;5(1):85. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0182-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32528035 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of exosomes in cancer therapy: progress and challenges.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jan 13;24(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02215-4. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39806451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Composition of Conditioned Media from Radioresistant and Chemoresistant Cancer Cells Reveals miRNA and Other Secretory Factors Implicated in the Development of Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 19;24(22):16498. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216498. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003688 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

