Safety Evaluation of Protective Equipment for the Forearm, Shin, Hand and Foot in Taekwondo
- PMID: 31191109
- PMCID: PMC6543987
Safety Evaluation of Protective Equipment for the Forearm, Shin, Hand and Foot in Taekwondo
Abstract
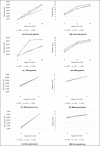
The objective of the study was to evaluate and compare different brands of forearm, shin, hand and foot protective equipment used in Taekwondo. The most popular brands of large forearm, shin, hand and foot protectors (D®, A®, K ®), approved by the World Taekwondo and Korean Taekwondo Association, were examined. A drop test was used to test the protective equipment using impact levels of 3J, 9J, 12J and 15J for the forearm and shin guards, and 3J and 9J for the hand and foot protectors. The protective equipment was hit ten times from each of the designated drop heights. The drop test is described in the European standards manual of protective equipment for martial arts (SRPS EN 13277-2). The maximum force (MF) and impulse were lowest for brand K® (2610.3 ± 1474.1 N), and brand A® (9.6 ± 3.1 Ns), respectively, for the forearm guards; for brand A® (2053.4 ± 1267.1 N) and brand K® (9.8 ± 3.5 Ns), respectively, for the shin guards; for brand K® (4486.5 ± 1718.4 N), and brand A® (6.3 ± 1.1 Ns), respectively for the hand protectors; and for brand A® (3733.7 ± 2465.3 N), and brand D® (6.8 ± 0.6 Ns), respectively, for the foot protectors. For the forearm guard brand and impact level, there was a significant interaction effect for the MF (F=42.44, η2=.677, p <0.001) and impulse (F = 33.97, η2 = 0.626, p <0.001). Based on the MF, brand K® performed the best for the forearm guards and hand protectors, and brand A®, for the shin guards and foot protectors. The best results for the impulse were for brand A® (forearm guards and hand protectors), brand K® (shin guards) and brand D® (foot protectors).
Keywords: Injury prevention; PSS; Taekwondo rules; protectors; safety.
Figures

References
-
- Arthur L.E. (1982) Karate protective equipment. In: Google Patents.
-
- Bae Y.S. (2013) Relationship between the impact value of electronic body protector and the impact force of force platform in the Taekwondo. Korean Journal of Sport Biomechanics 23(2), 125-130.
-
- Beumer A., Van Hemert W.L.W., Swierstra B.A., Jasper L.E., Belkoff S.M. (2003) A biomechanical evaluation of the tibiofibular and tibiotalar ligaments of the ankle. Foot and Ankle International 24(5), 426-429. - PubMed
-
- Bir C.A., Cassatta S.J., Janda D.H. (1995) An analysis and comparison of soccer shin guards. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine 5(2), 95-99. - PubMed
-
- Bromley S.J., Drew M.K., Talpey S., McIntosh A.S., Finch C.F. (2018) A systematic review of prospective epidemiological research into injury and illness in Olympic combat sport. British Journal of Sports Medicine 52(1), 8-16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
