Kounis syndrome secondary to gadolinium contrast agent
- PMID: 31191145
- PMCID: PMC6541077
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2019.1581319
Kounis syndrome secondary to gadolinium contrast agent
Abstract
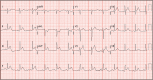
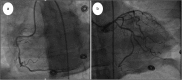
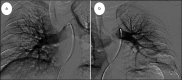
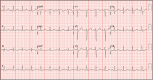
Cases of coronary artery spasm secondary to contrast agent use are rarely reported. Herein, we report the case of a 53-year-old woman who developed chest pain, dyspnea, and bradycardia and quickly become unresponsive after magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. A heart monitor showed ST elevation, and an electrocardiogram showed ST elevations in leads II, III, aVF, V3, and V4 and ST segment depression in lead I. Urgent left heart catheterization revealed no evidence of obstructive coronary artery disease or pulmonary embolism. A few days later, she was discharged from the hospital with no symptoms. A type I variant of Kounis syndrome was diagnosed.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Kounis syndrome; allergy; contrast medium–induced coronary vasospasm; coronary hypersensitivity disorder.
Figures
References
-
- Kounis NG, Zavras GM. Histamine-induced coronary artery spasm: the concept of allergic angina. Br J Clin Pract. 1991;45:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Pfister CW, Plice SG. Acute myocardial infarction during a prolonged allergic reaction to penicillin. Am Heart J. 1950;40:945–947. - PubMed
-
- Gázquez V, Dalmau G, Gaig P, Gómez C, Navarro S, Mercé J. Kounis syndrome: report of 5 cases. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol, 2010;20:162–165. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
