The Effect of Nitric Oxide on Remote Ischemic Preconditioning in Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats
- PMID: 31191188
- PMCID: PMC6542129
- DOI: 10.1177/1559325819853651
The Effect of Nitric Oxide on Remote Ischemic Preconditioning in Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats
Abstract
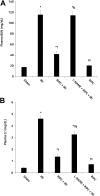
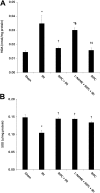
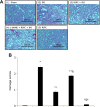
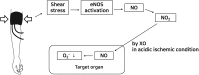
Although remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC) is an organ-protective maneuver from subsequent ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) by application of brief ischemia and reperfusion to other organs, its mechanism remains unclear. However, it is known that RIPC reduces the heart, brain, and liver IRI, and that nitric oxide (NO) is involved in the mechanism of this effect. To identify the role of NO in the protective effect of RIPC in renal IRI, this study examined renal function, oxidative status, and histopathological changes using N-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), an NO synthase inhibitor. Remote ischemic preconditioning was produced by 3 cycles of 5 minutes ischemia and 5 minutes reperfusion. Blood urea nitrogen, creatinine (Cr), and renal tissue malondialdehyde levels were lower, histopathological damage was less severe, and superoxide dismutase level was higher in the RIPC + IRI group than in the IRI group. The renoprotective effect was reversed by L-NAME. Obtained results suggest that RIPC before renal IRI contributes to improvement of renal function, increases antioxidative marker levels, and decreases oxidative stress marker levels and histopathological damage. Moreover, NO is likely to play an important role in this protective effect of RIPC on renal IRI.
Keywords: ischemia reperfusion injury; nitric oxide; remote ischemic preconditioning.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning in Hepatic Ischemic Reperfusion Injury.Dose Response. 2020 Aug 13;18(3):1559325820946923. doi: 10.1177/1559325820946923. eCollection 2020 Jul-Sep. Dose Response. 2020. PMID: 32848526 Free PMC article.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning: a novel protective method from ischemia reperfusion injury--a review.J Surg Res. 2008 Dec;150(2):304-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.12.747. Epub 2008 Jan 22. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 19040966 Review.
-
Repeated remote ischemic preconditioning and isoflurane anesthesia in an experimental model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.BMC Anesthesiol. 2017 Jan 28;17(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12871-017-0310-x. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 28129737 Free PMC article.
-
Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Decreases the Magnitude of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury on a Swine Model of Supraceliac Aortic Cross-Clamping.Ann Vasc Surg. 2018 Apr;48:241-250. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Ann Vasc Surg. 2018. PMID: 28887256
-
Protocols and mechanisms for remote ischemic preconditioning: a novel method for reducing ischemia reperfusion injury.Transplantation. 2007 Aug 27;84(4):445-58. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000228235.55419.e8. Transplantation. 2007. PMID: 17713425 Review.
Cited by
-
Nontopical Nitrates in Flap Perfusion and Delay Phenomenon.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 Jun 17;12(6):e5918. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005918. eCollection 2024 Jun. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 38911578 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of Class III Alcohol Dehydrogenase 5: Turning Remote Ischemic Conditioning Effective in a Diabetic Stroke Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 18;11(10):2051. doi: 10.3390/antiox11102051. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290774 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective effects of remote ischemic preconditioning on acute kidney injury induced by repeated tourniquet application in patients undergoing extremity surgery.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 20;11:1477099. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1477099. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39760033 Free PMC article.
-
Remote Ischemic Conditioning Enhances Collateral Circulation Through Leptomeningeal Anastomosis and Diminishes Early Ischemic Lesions and Infarct Volume in Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion.Transl Stroke Res. 2024 Feb;15(1):41-52. doi: 10.1007/s12975-022-01108-2. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Transl Stroke Res. 2024. PMID: 36441491
-
Efficacy of low extra-abdominal aortic block in cesarean section for placenta accreta spectrum disorders and its effect on the expression of MDA and SOD.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Aug 28;47(8):1129-1135. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.220118. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36097781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang S-S, Wei F-C, Hung L-M. Ischemic preconditioning attenuates postischemic leukocyte—endothelial cell interactions: role of nitric oxide and protein kinase C. Circ J. 2006;70(8):1070–1075. - PubMed
-
- Olguner C, Koca U, Kar A, et al. Ischemic preconditioning attenuates the lipid peroxidation and remote lung injury in the rat model of unilateral lower limb ischemia reperfusion. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006;50(2):150–155. - PubMed
-
- Xia Z, Li H, Irwin MG. Myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury: the challenge of translating ischaemic and anaesthetic protection from animal models to humans. Br J Anaesth. 2016;117(suppl 2):ii44–ii62. - PubMed
-
- Matin SF, Novick AC. Renal dysfunction associated with staged bilateral partial nephrectomy: the importance of operative positioning. J Urol. 2001;165(3):880–881. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

