Ginseng-Angelica-Sansheng-Pulvis Boosts Neurogenesis Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Neurological Deficiency
- PMID: 31191223
- PMCID: PMC6549519
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00515
Ginseng-Angelica-Sansheng-Pulvis Boosts Neurogenesis Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Neurological Deficiency
Abstract
Background: The traditional Chinese medicine Ginseng-Angelica-Shanseng-Pulvis (GASP) has been used to treat stroke for 300 years. This present study investigated if it can induce increases in neurogenesis following cerebral ischemic injury.
Methods: Rats following middle cerebral artery occlusion were orally treated with high, medium, and low doses of a standardized GASP extract.
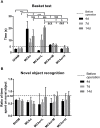
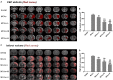
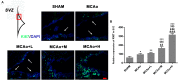
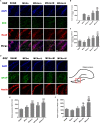
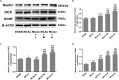
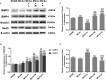
Results: After 14 days, treatment with GASP improved regional blood flow and infarction volume by magnetic resonance imaging scanning, enhanced Ki67+ expression in the subventricular zone, increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) secretion, Nestin, and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 2/4 expressions in the hippocampus in a dose-dependent manner. Interestingly, low-dose treatment with GASP downregulated doublecortin and Notch1 expressions in the hippocampus, as well as upregulated glial fibrillary acidic protein expression in the subgranular zone and hairy and enhancer of split (Hes) 5 expression in the hippocampus, while treatment with middle and high doses of GASP reversed these results. Meanwhile, the consumed time was shortened in the basket test and the adhesive removal test and the spending time on exploring novel objects was prolonged by GASP treatment whose effects were more obvious at day 14 post-ischemia.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that treatment with GASP increases neurogenesis and ameliorates sensorimotor functions and recognition memory. We hypothesize that these effects are thought be mediated by an effect on the BMP2/4 pathway and Notch1/Hes5 signal. Due to its beneficial efficacy, GASP can be recognized as an alternative therapeutic agent for ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Ginseng-Angelica-Sansheng-Pulvis; ischemic stroke; neural differentiation; neurogenesis; neurological deficiency.
Figures

References
-
- Chen Y. F., Wang Y. W., Huang W. S., Lee M. M., Wood W. G., Leung Y. M., et al. (2016). Trans-cinnamaldehyde, an essential oil in cinnamon powder, ameliorates cerebral ischemia-induced brain injury via inhibition of neuroinflammation through attenuation of inos, cox-2 expression and nfκ-b signaling pathway. Neuromolecular Med. 18 322–333. 10.1007/s12017-016-8395-9 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

