The Neuroprotective Effect of Hemin and the Related Mechanism in Sevoflurane Exposed Neonatal Rats
- PMID: 31191229
- PMCID: PMC6546893
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00537
The Neuroprotective Effect of Hemin and the Related Mechanism in Sevoflurane Exposed Neonatal Rats
Abstract
Background: Many studies have reported that sevoflurane can increase neuronal apoptosis and result in cognitive deficits in rodents. Although neurotoxicity may be associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, the exact mechanism remains unclear. In order to evaluate potential treatment therapies, we studied the effects of hemin on neurotoxicity of neonatal rat sevoflurane exposure.
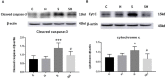
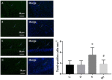
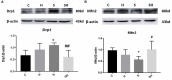
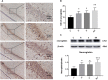
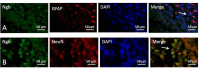
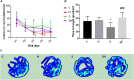
Methods: Postnatal day (P) seven rats were assigned randomly to four groups; (1) group C: non-anesthesia, (2) group H: intraperitoneal hemin (50 mg kg-1) treatment on days 5 and 6, (3) group S: 3% sevoflurane exposure for 4 h, and (4) group SH: hemin treatment + sevoflurane exposure. The expression of neuroglobin in neonatal hippocampus was determined by western blot and immunohistochemistry. Neuroglobin was localized by immunofluorescence. Western blot for the expression of cleaved caspase-3 and TUNEL were used to detect neonatal hippocampal apoptosis, and cytochrome c was used to evaluate mitochondrial function. Drp-1 and Mfn-2 immunoblotting were used to assess mitochondrial dynamics. The Morris water maze test was performed to detect cognitive function in the rats on P30.
Results: Exposure to sevoflurane increased the expression of cleaved caspase-3, cytochrome c, and Drp1 in the neonatal hippocampus and resulted in cognitive deficiency but decreased expression of Mfn2. Hemin reduced apoptosis, improved mitochondrial dynamics and ameliorated the cognitive impairment caused by sevoflurane exposure.
Conclusion: Hemin reduced neuronal apoptosis, improved mitochondrial dynamics and protected against cognitive deficits induced by sevoflurane in neonatal rats. This neuroprotective effect may be achieved by increasing the expression of neuroglobin.
Keywords: hemin; mitochondria; neuroglobin; neurotoxicity; sevoflurane.
Figures
References
-
- Antao S. T., Duong T. T., Aran R., Witting P. K. (2010). Neuroglobin overexpression in cultured human neuronal cells protects against hydrogen peroxide insult via activating phosphoinositide-3 kinase and opening the mitochondrial K(ATP) channel. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 13 769–781. 10.1089/ars.2009.2977 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

