The Inflammatory Response After Ischemic Stroke: Targeting β2 and β1 Integrins
- PMID: 31191232
- PMCID: PMC6546847
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00540
The Inflammatory Response After Ischemic Stroke: Targeting β2 and β1 Integrins
Abstract
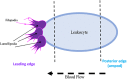
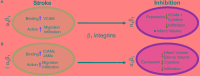
Ischemic stroke is a leading cause of death and disability with limited therapeutic options. Resulting inflammatory mechanisms after reperfusion (removal of the thrombus) result in cytokine activation, calcium influx, and leukocytic infiltration to the area of ischemia. In particular, leukocytes migrate toward areas of inflammation by use of integrins, particularly integrins β1 and β2. Integrins have been shown to be necessary for leukocyte adhesion and migration, and thus are of immediate interest in many inflammatory diseases, including ischemic stroke. In this review, we identify the main integrins involved in leukocytic migration following stroke (α L β2, αDβ2, α4β1, and α5β1) and targeted clinical therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: clinical trial results; inflammation; integrins; ischemic stroke; leukocytes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Leukocyte integrins: role in leukocyte recruitment and as therapeutic targets in inflammatory disease.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Mar;147:123-135. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.11.008. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25448040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
beta1 integrins are critically involved in neutrophil locomotion in extravascular tissue In vivo.J Exp Med. 1998 Jun 15;187(12):2091-6. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.12.2091. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9625769 Free PMC article.
-
A novel form of integrin dysfunction involving beta1, beta2, and beta3 integrins.J Clin Invest. 2003 Jan;111(1):51-60. doi: 10.1172/JCI14076. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12511588 Free PMC article.
-
Cell adhesion molecules, leukocyte trafficking, and strategies to reduce leukocyte infiltration.J Vet Intern Med. 2001 Nov-Dec;15(6):516-29. doi: 10.1892/0891-6640(2001)015<0516:camlta>2.3.co;2. J Vet Intern Med. 2001. PMID: 11817056 Review.
-
JAK2-V617F promotes venous thrombosis through β1/β2 integrin activation.J Clin Invest. 2018 Oct 1;128(10):4359-4371. doi: 10.1172/JCI90312. Epub 2018 Jul 19. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 30024857 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Flavonoids Icaritin and Icariin Protect against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion-Associated Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Accumulation in an Ischemic Stroke Mouse Model.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 19;9(11):1719. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111719. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829948 Free PMC article.
-
Negative Regulators of Inflammation Response to the Dynamic Expression of Cytokines in DF-1 and MDCK Cells Infected by Avian Influenza Viruses.Inflammation. 2022 Apr;45(2):573-589. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01568-y. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Inflammation. 2022. PMID: 34581936
-
A myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) inhibitor peptide attenuates neutrophil outside-in β2-integrin activation and signaling.Cell Adh Migr. 2023 Dec;17(1):1-16. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2023.2233204. Cell Adh Migr. 2023. PMID: 37439125 Free PMC article.
-
New Drug Targets to Prevent Death Due to Stroke: A Review Based on Results of Protein-Protein Interaction Network, Enrichment, and Annotation Analyses.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 9;22(22):12108. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212108. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34829993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relevance of Reperfusion Stroke Therapy for miR-9-3p and miR-9-5p Expression in Acute Stroke-A Preliminary Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 27;25(5):2766. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052766. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arumugam T. V., Salter J. W., Chidlow J. H., Ballantyne C. M., Kevil C. G., Granger D. N. (2004). Contributions of LFA-1 and Mac-1 to brain injury and microvascular dysfunction induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 287 H2555–H2560. 10.1152/ajpheart.00588.2004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Becker K. (2002). Anti-leukocyte antibodies: leukarrest (Hu23F2G) and enlimomab (R6.5) in acute stroke. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 18(Suppl. 2), 18–22. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

