Resilience and Vulnerability to Trauma: Early Life Interventions Modulate Aversive Memory Reconsolidation in the Dorsal Hippocampus
- PMID: 31191245
- PMCID: PMC6546926
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00134
Resilience and Vulnerability to Trauma: Early Life Interventions Modulate Aversive Memory Reconsolidation in the Dorsal Hippocampus
Abstract
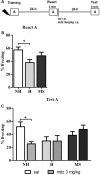
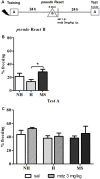
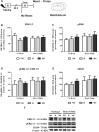
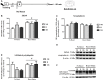
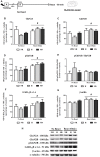
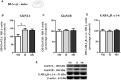
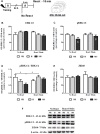
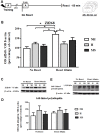
Early life experiences program lifelong responses to stress. In agreement, resilience and vulnerability to psychopathologies, such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), have been suggested to depend on the early background. New therapies have targeted memory reconsolidation as a strategy to modify the emotional valence of traumatic memories. Here, we used animal models to study the molecular mechanism through which early experiences may later affect aversive memory reconsolidation. Handling (H)-separation of pups from dams for 10 min-or maternal separation (MS) - 3-h separation-were performed from PDN1-10, using non-handled (NH) litters as controls. Adult males were trained in a contextual fear conditioning (CFC) task; 24 h later, a short reactivation session was conducted in the conditioned or in a novel context, followed by administration of midazolam 3 mg/kg i.p. (mdz), known to disturb reconsolidation, or vehicle; a test session was performed 24 h after. The immunocontent of relevant proteins was studied 15 and 60 min after memory reactivation in the dorsal hippocampus (dHc) and basolateral amygdala complex (BLA). Mdz-treated controls (NH) showed decreased freezing to the conditioned context, consistent with reconsolidation impairment, but H and MS were resistant to labilization. Additionally, MS males showed increased freezing to the novel context, suggesting fear generalization; H rats showed lower freezing than the other groups, in accordance with previous suggestions of reduced emotionality facing adversities. Increased levels of Zif268, GluN2B, β-actin and polyubiquitination found in the BLA of all groups suggest that memory reconsolidation was triggered. In the dHc, only NH showed increased Zif268 levels after memory retrieval; also, a delay in ERK1/2 activation was found in H and MS animals. We showed here that reconsolidation of a contextual fear memory is insensitive to interference by a GABAergic drug in adult male rats exposed to different neonatal experiences; surprisingly, we found no differences in the reconsolidation process in the BLA, but the dHc appears to suffer temporal desynchronization in the engagement of reconsolidation. Our results support a hippocampal-dependent mechanism for reconsolidation resistance in models of early experiences, which aligns with current hypotheses for the etiology of PTSD.
Keywords: basolateral amygdala; dorsal hippocampus; fear memory; maternal separation; neonatal handling; reconsolidation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aversive memory reactivation: A possible role for delta oscillations in the hippocampus-amygdala circuit.J Neurosci Res. 2023 Jan;101(1):48-69. doi: 10.1002/jnr.25127. Epub 2022 Sep 21. J Neurosci Res. 2023. PMID: 36128957
-
Taking advantage of fear generalization-associated destabilization to attenuate the underlying memory via reconsolidation intervention.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Dec 15;181:108338. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108338. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 33002500
-
Stress-induced resistance to the fear memory labilization/reconsolidation process. Involvement of the basolateral amygdala complex.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Oct;109:349-356. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.06.033. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 27378335
-
Different temporal windows for CB1 receptor involvement in contextual fear memory destabilisation in the amygdala and hippocampus.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 15;14(1):e0205781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205781. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30645588 Free PMC article.
-
Lose the fear and boost the everyday memory through memory destabilisation and reconsolidation.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Nov;190:134-139. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.09.019. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 36202323 Review.
Cited by
-
Interfering With Contextual Fear Memories by Post-reactivation Administration of Propranolol in Mice: A Series of Null Findings.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jun 27;16:893572. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.893572. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35832291 Free PMC article.
-
At the Crossroad Between Resiliency and Fragility: A Neurodevelopmental Perspective on Early-Life Experiences.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Apr 7;16:863866. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.863866. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35465609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deficits in hippocampal-dependent memory across different rodent models of early life stress: systematic review and meta-analysis.Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Apr 20;11(1):231. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01352-4. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33879774 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hippocampus in memory reactivation: an implication for a therapeutic target against opioid use disorder.Curr Addict Rep. 2022;9(2):67-79. doi: 10.1007/s40429-022-00407-w. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Curr Addict Rep. 2022. PMID: 35223369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-step pharmacological intervention for traumatic-like memories: implications from D-cycloserine and cannabidiol or clonidine in male and female rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Sep;241(9):1827-1840. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06596-8. Epub 2024 May 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38691149
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

