Dual Role of Autophagy in Diseases of the Central Nervous System
- PMID: 31191249
- PMCID: PMC6548059
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00196
Dual Role of Autophagy in Diseases of the Central Nervous System
Abstract
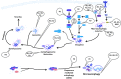
Autophagy is a vital lysosomal degradation and recycling pathway in the eukaryotic cell, responsible for maintaining an intricate balance between cell survival and cell death, necessary for neuronal survival and function. This dual role played by autophagy raises the question whether this process is a protective or a destructive pathway, the contributor of neuronal cell death or a failed attempt to repair aberrant processes? Deregulated autophagy at different steps of the pathway, whether excessive or downregulated, has been proposed to be associated with neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's-, Huntington's-, and Parkinson's-disease, known for their intracellular accumulation of protein aggregates. Recent observations of impaired autophagy also appeared in psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder suggesting an additional contribution to the pathophysiology of mental illness. Here we review the current understanding of autophagy's role in various neuropsychiatric disorders and, hitherto, the prevailing new potential autophagy-related therapeutic strategies for their treatment.
Keywords: autophagy; central nervous system; lithium; neurodegenerative diseases; psychiatric disorders.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2016). DSM-5 Classification. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- Anglade P., Vyas S., Javoy-Agid F., Herrero M. T., Michel P. P., Marquez J., et al. (1997). Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol. Histopathol. 12 25–31. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

