Reciprocal Relationship Between HDAC2 and P-Glycoprotein/MRP-1 and Their Role in Steroid Resistance in Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome
- PMID: 31191307
- PMCID: PMC6540828
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00558
Reciprocal Relationship Between HDAC2 and P-Glycoprotein/MRP-1 and Their Role in Steroid Resistance in Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome
Abstract
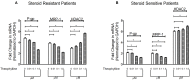
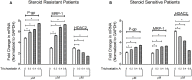
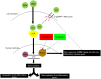
Background: Reduced HDACs levels have been reported in steroid resistant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchial asthma patients. P-glycoprotein (P-gp) over expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) has been reported in patients with steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome (NS). Whether and how HDACs and P-gp are linked with each other is not clear, especially in NS patients. Aim: To evaluate mRNA expression of P-gp/MRP-1 and HDAC2 in PBMCs of steroid sensitive (SSNS) and steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) patients, and determine the relationship between expression of HDAC2 and P-gp/ MRP-1in NS patients. Methods: Twenty subjects (10 in each group), SSNS (mean age 7.54 ± 3.5 years), and SRNS (mean age 8.43 ± 3.8 years) were recruited. mRNA expression of HDAC2 and P-gp/MRP-1 was studied by quantitative real time PCR. PBMCs were treated with Theophylline, 1 μM, and Trichostatin A, 0.8 μM, for 48 h for induction and suppression of HDAC2, respectively. Results: At baseline, expression of P-gp (4.79 ± 0.10 vs. 2.13 ± 0.12, p < 0.0001) and MRP-1 (3.99 ± 0.08 vs. 1.99 ±0.11, p < 0.0001) on PBMCs were increased whereas, HDAC2 mRNA levels (2.97 ± 0.15 vs. 6.02 ± 0.13, p < 0.0001) were significantly decreased in SRNS as compared to that of SSNS patients. Compared to baseline, theophylline reduced mRNA expression of P-gp and MRP-1 (fold change 2.65 and 2.21, * p < 0.0001 in SRNS) (fold change 1.25, 1.24, * p < 0.0001 in SSNS), respectively. However, it increased the expression of HDAC2 (fold change 5.67, * p < 0.0001 in SRNS) (fold change 6.93, * p < 0.0001 in SSNS). Compared to baseline, TSA treatment increased mRNA levels of P-gp and MRP-1 (fold change 7.51, 7.31, * p < 0.0001 in SRNS) and (fold change 3.49, 3.35, * p < 0.0001 in SSNS), respectively. It significantly decreased the level of HDAC2 (fold change 1.50, * p < 0.0001 in SRNS) (fold change 2.53, * p < 0.0001 in SSNS) patients. Conclusion: Reduced HDAC2 and increased P-gp/MRP-1 activity may play a role in response to steroids in childhood NS. HDAC2 and P-gp/MRP-1 are in reciprocal relationship with each other.
Keywords: HDAC inhibitor and HDAC stimulator; P-glycoprotein (P-gp); histone deacetylase2 (HDAC2); multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP-1); steroid resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of P-glycoprotein and MRP-1 are pharmacogenomic biomarkers to determine steroid resistant phenotype in childhood idiopathic nephrotic syndrome.Pharmacogenomics J. 2021 Oct;21(5):566-573. doi: 10.1038/s41397-021-00233-9. Epub 2021 May 19. Pharmacogenomics J. 2021. PMID: 34011975
-
Histone deacetylase-2 expression and activity in children with nephrotic syndrome with different glucocorticoid response.Pediatr Nephrol. 2018 Feb;33(2):269-276. doi: 10.1007/s00467-017-3791-4. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29098400
-
[Interleukin-18 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2009 May;11(5):337-40. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19470251 Chinese.
-
Genetics of childhood steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome.Pediatr Nephrol. 2017 Sep;32(9):1481-1488. doi: 10.1007/s00467-016-3456-8. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Pediatr Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27470160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Difficult-to-treat idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: established drugs, open questions and future options.Pediatr Nephrol. 2018 Oct;33(10):1641-1649. doi: 10.1007/s00467-017-3780-7. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 28879428 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Th17 Lymphocyte Populations, Th17.1 and PD1+Th17, are Increased in Takayasu Arteritis, and Both Th17 and Th17.1 Sub-Populations Associate with Active Disease.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Mar 1;15:1521-1541. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S355881. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35256852 Free PMC article.
-
P-glycoprotein: new insights into structure, physiological function, regulation and alterations in disease.Heliyon. 2022 Jun 22;8(6):e09777. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09777. eCollection 2022 Jun. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35789865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Panax notoginseng saponins reverse P-gp-mediated steroid resistance in lupus: involvement in the suppression of the SIRT1/FoxO1/MDR1 signalling pathway in lymphocytes.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jan 12;22(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03499-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35022006 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Interleukin-17 and Glucocorticoid Receptor-β Expression in Interstitial Lung Diseases and Corticosteroid Insensitivity.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 5;13:905727. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.905727. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35865549 Free PMC article.
-
Tacrolimus induces remission in refractory and relapsing lupus nephritis by decreasing P-glycoprotein expression and function on peripheral blood lymphocytes.Rheumatol Int. 2022 Aug;42(8):1347-1354. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-05057-1. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Rheumatol Int. 2022. PMID: 34993577
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

