Time Series Gene Expression Profiling and Temporal Regulatory Pathway Analysis of Angiotensin II Induced Atrial Fibrillation in Mice
- PMID: 31191333
- PMCID: PMC6548816
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00597
Time Series Gene Expression Profiling and Temporal Regulatory Pathway Analysis of Angiotensin II Induced Atrial Fibrillation in Mice
Abstract
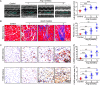
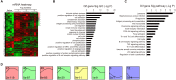
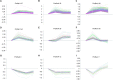
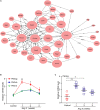
Background/Aim: Angiotensin II (Ang II) and hypertension play critical roles in the pathogenesis of the atrial remodeling that contributes to atrial fibrillation (AF). However, the gene expression profiles and signaling pathways in atria during the development of AF induced by Ang II remain unknown. Methods: Wild-type male mice (C57BL/6 background, 10 weeks old) were administered an infusion of Ang II (2000 ng/kg/min) using an osmotic pump for 1, 2, and 3 weeks. Blood pressure (BP) was measured by the tail-cuff method. AF was induced and recorded. Atrial enlargement and remodeling were examined by echocardiography and Masson's trichrome staining. Time-series microarray analyses were conducted to examine gene expression profiles and pathways. Results: Ang II infusion resulted in marked elevation of systolic BP, increased AF incidence and duration, atrial enlargement, fibrosis, and atrial infiltration of myofibroblasts and F4/80-positive macrophages in a time-dependent manner. Microarray results showed that 1,719 genes were differentially expressed in the atrium at weeks 1, 2, and 3 after Ang II infusion. Gene ontology showed that these genes participate mainly in immune system processes, and regulation of cell migration, cell adhesion, complement activation, and the inflammatory response. Significant pathways included lysosomal and phagosomal pathways, which are involved in antigen processing and presentation, as well as chemokine signaling, and extracellular matrix-receptor interaction, which are known to play important roles in Ang II-induced AF. Moreover, these differentially expressed genes were classified into 50 profiles by hierarchical cluster analysis. Of these, eight profiles were significant and contained a total of 1,157 genes. Gene co-expression network analysis identified that Pik3cg (also known as phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 3) was localized in the core of the gene network, and was the most highly expressed among the Pik3 isoforms at different time points. Conclusion: The present findings revealed that many genes are involved in Ang II-induced AF, and highlighted that Pik3cg may play a central role in this disease.
Keywords: Pik3cg; angiotensin II; atrial fibrillation; microarray; time series gene expression profiling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gene expression profile in the early stage of angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling: a time series microarray study in a mouse model.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(2):467-76. doi: 10.1159/000369712. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25613478
-
Analysis of Genes Related to Angiotensin II-Induced Arterial Injury Using a Time Series Microarray.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(3):983-992. doi: 10.1159/000491966. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30036880
-
Time series RNA-seq analysis identifies MAPK10 as a critical gene in diabetes mellitus-induced atrial fibrillation in mice.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022 Jul;168:70-82. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2022.04.013. Epub 2022 Apr 27. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35489387
-
Gallic Acid Ameliorates Angiotensin II-Induced Atrial Fibrillation by Inhibiting Immunoproteasome- Mediated PTEN Degradation in Mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 30;8:594683. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.594683. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33251220 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine Receptor CXCR-2 Initiates Atrial Fibrillation by Triggering Monocyte Mobilization in Mice.Hypertension. 2020 Aug;76(2):381-392. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.14698. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32639881
Cited by
-
Overview of programmed electrical stimulation to assess atrial fibrillation susceptibility in mice.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 11;14:1149023. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1149023. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37113690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRD4 Silencing Protects Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy by Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB and Activating Nrf2-HO-1 Pathways.Cardiol Res Pract. 2022 Sep 19;2022:8372707. doi: 10.1155/2022/8372707. eCollection 2022. Cardiol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 36247184 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II Stimulates the Proliferation and Migration of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Through Angiotensin Type 1 Receptors.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 8;11:560170. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.560170. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33013481 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Ventilation-Induced Diaphragm Fibrosis through the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-γ in a Murine Bleomycin-Induced Acute Lung Injury Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 8;25(12):6370. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126370. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928077 Free PMC article.
-
β-Hydroxybutyrate and Citrate Synthase as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers in Aging-Related Atrial Fibrillation.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025 Feb;18(1):133-145. doi: 10.1007/s12265-024-10569-9. Epub 2024 Nov 5. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39499445 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

