Physical Activity in Natural Environments Is Associated With Motivational Climate and the Prevention of Harmful Habits: Structural Equation Analysis
- PMID: 31191381
- PMCID: PMC6548877
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01113
Physical Activity in Natural Environments Is Associated With Motivational Climate and the Prevention of Harmful Habits: Structural Equation Analysis
Abstract
Background: Practicing physical activity in a natural environment has various benefits that make it an ideal setting to develop healthy behaviors and thereby diminish unhealthy habits. The objective of this study was to develop and verify an explicative model for motivational climate in sport, considering its potential influence on alcohol and tobacco consumption.
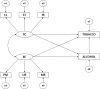
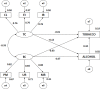
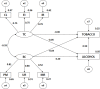
Methods: The study included 2273 adolescents from Granada (Spain), analyzing motivational climate (PMCSQ-2), alcohol consumption (AUDIT) and tobacco consumption (FTND). Multi-group structural equation modeling was conducted, yielding an excellent fit (χ2 = 168.170; gl = 32; p = 0.00; CFI = 0.972; NFI = 0.966; IFI = 0.972; RMSEA = 0.045).
Results: The main findings were: a negative relationship between task climate and alcohol consumption among students practicing physical activities in a natural environment; a positive relationship between ego climate and alcohol consumption among those practicing other types of physical activity; and a positive and direct relationship between alcohol and tobacco consumption, which was stronger among those who did not practice physical activity in a natural environment.
Conclusion: We conclude that physical-sport activity practiced in nature is a key to acquiring healthy patterns characterized by intrinsic motivations in sport and lower consumption of harmful substances.
Keywords: alcohol; motivation; natural environment; physical activity; tobacco.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Motivational Climate in Sport Is Associated with Life Stress Levels, Academic Performance and Physical Activity Engagement of Adolescents.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Apr 3;16(7):1198. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16071198. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30987123 Free PMC article.
-
Motivational Climate Is Associated with Use of Video Games and Violence in Schoolchildren: A Structural Equation Model According to Healthy Behaviors.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Feb 17;17(4):1272. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17041272. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32079182 Free PMC article.
-
Explanatory model of motivational climate, self-concept and emotional intelligence in primary school students: Structural equation analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 8;10(22):e40214. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40214. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39584085 Free PMC article.
-
[Physical activity, Mediterranean diet, maximal oxygen uptake and motivational climate towards sports in schoolchildren from the province of Granada: a structural equation model].Nutr Hosp. 2018 Jun 6;35(4):774-781. doi: 10.20960/nh.1511. Nutr Hosp. 2018. PMID: 30070863 Spanish.
-
Motivational Climate and Physical Activity: A Multigroup Analysis in Romanian and Spanish University Students.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jun 5;16(11):2013. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16112013. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31195759 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the healing power of nature: a review of natural interventions in substance abuse treatment and prevention.Environ Health Prev Med. 2024;29:64. doi: 10.1265/ehpm.24-00145. Environ Health Prev Med. 2024. PMID: 39537154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship Between the Practice of Physical Activity and Physical Fitness in Physical Education Students: The Integrated Regulation As a Mediating Variable.Front Psychol. 2020 Jul 29;11:1910. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01910. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32849119 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-lagged panel relationship between physical activity atmosphere, psychological resilience and mobile phone addiction on college students.Sci Rep. 2025 May 13;15(1):16599. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97848-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40360737 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Activity Behaviour in People with COPD Residing in Spain: A Cross-Sectional Analysis.Lung. 2019 Dec;197(6):769-775. doi: 10.1007/s00408-019-00287-4. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Lung. 2019. PMID: 31686208
-
Documents Publication Evolution (1990-2022) Related to Physical Activity and Healthy Habits, a Bibliometric Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;11(12):1669. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11121669. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372787 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amaro L. A., Prado P. A., Paiano R., Verardi C. E., Larizzatti M. F., Hirota V. B. (2017). Correlation between goal orientation and attitudes of Brazilian elite swimmers. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 17 783–788. 10.7752/jpes.2017.02118 - DOI
-
- Arslanoglu C. (2016). Relationship between target orientations and perceived motivational climate levels of students engaged in individual and team sports activities. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 11 3311–3318.
-
- Barrett P., Imamura F., Brage S., Griffin S. J., Wareham N. J., Forouhi N. G. (2017). Sociodemographic, lifestyle and behavioral factors associated with consumption of sweetened beverages among adults in cambridgeshire, UK: the fenland study. Public Health Nutr. 20 2766–2777. 10.1017/S136898001700177X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

