Apolipoprotein E Homozygous ε4 Allele Status: A Deteriorating Effect on Visuospatial Working Memory and Global Brain Structure
- PMID: 31191441
- PMCID: PMC6545528
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00552
Apolipoprotein E Homozygous ε4 Allele Status: A Deteriorating Effect on Visuospatial Working Memory and Global Brain Structure
Abstract
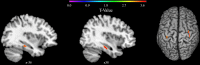
Theoretical background: The Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 genotype is known to be one of the strongest single-gene predictors for Alzheimer disease, which is characterized by widespread brain structural degeneration progressing along with cognitive impairment. The ε4 allele status has been associated with brain structural alterations and lower cognitive ability in non-demented subjects. However, it remains unclear to what extent the visuospatial cognitive domain is affected, from what age onward changes are detectable and if alterations may interact with cognitive deficits in major depressive disorder (MDD). The current work investigated the effect of APOE ε4 homozygosity on visuospatial working memory (vWM) capacity, and on hippocampal morphometry. Furthermore, potential moderating roles of age and MDD were assessed. Methods: A sample of n = 31 homozygous ε4 carriers was contrasted with n = 31 non-ε4 carriers in a cross-sectional design. The sample consisted of non-demented, young to mid-age participants (mean age = 34.47; SD = 13.48; 51.6% female). Among them were n = 12 homozygous ε4 carriers and n = 12 non-ε4 carriers suffering from MDD (39%). VWM was assessed using the Corsi block-tapping task. Region of interest analyses of hippocampal gray matter density and volume were conducted using voxel-based morphometry (CAT12), and Freesurfer, respectively. Results: Homozygous ε4 carriers showed significantly lower Corsi span capacity than non-ε4 carriers did, and Corsi span capacity was associated with higher gray matter density of the hippocampus. APOE group differences in hippocampal volume could be detected but were no longer present when controlling for total intracranial volume. Hippocampal gray matter density did not differ between APOE groups. We did not find any interaction effects of age and MDD diagnosis on hippocampal morphometry. Conclusion: Our results point toward a negative association of homozygous ε4 allele status with vWM capacity already during mid-adulthood, which emerges independently of MDD diagnosis and age. APOE genotype seems to be associated with global brain structural rather than hippocampus specific alterations in young- to mid-age participants.
Keywords: Alzheimer; apolipoprotein E; cognitive deficits; hippocampus; major depression; structural MRI; visuospatial working memory.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein E homozygous ε4 allele status: Effects on cortical structure and white matter integrity in a young to mid-age sample.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021 May;46:93-104. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2021.02.006. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33648793
-
Association between white matter hyperintensity severity and cognitive impairment according to the presence of the apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 allele in the elderly: retrospective analysis of data from the CREDOS study.J Clin Psychiatry. 2012 Dec;73(12):1555-62. doi: 10.4088/JCP.12m07702. Epub 2012 Oct 30. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23146133
-
APOE-ε4 risk variant for Alzheimer's disease modifies the association between cognitive performance and cerebral morphology in healthy middle-aged individuals.Neuroimage Clin. 2019;23:101818. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101818. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Neuroimage Clin. 2019. PMID: 30991302 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E ε4 Modulates Cognitive Profiles, Hippocampal Volume, and Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;45(3):781-95. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142556. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25624419
-
The Elusive Nature of APOE ε4 in Mid-adulthood: Understanding the Cognitive Profile.J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2017 Mar;23(3):239-253. doi: 10.1017/S1355617716000990. Epub 2017 Jan 6. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2017. PMID: 28059047 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between clinical symptoms and apolipoprotein A1 or apolipoprotein B levels is regulated by apolipoprotein E variant rs429358 in patients with chronic schizophrenia.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2021 Dec 20;20(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12991-021-00376-w. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34930329 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the APOE Gene Polymorphism with Depression in White Adults in the WHO "MONICA-Psychosocial" Program.J Pers Med. 2023 Aug 26;13(9):1306. doi: 10.3390/jpm13091306. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37763074 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Apolipoprotein E ε4 in Alzheimer's Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Voxel-Based Morphometry Studies.J Clin Neurol. 2024 Sep;20(5):469-477. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2024.0176. J Clin Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39227329 Free PMC article.
-
APOE ε4 influences cognitive decline positively in APP and negatively in PSEN1 mutation carriers with autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Neurol. 2022 Dec;29(12):3580-3589. doi: 10.1111/ene.15536. Epub 2022 Sep 11. Eur J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36039401 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of APOE ε2 on the Fractional Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuation in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Study Based on the Resting-State Functional MRI.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Apr 29;13:591347. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.591347. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33994988 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

