Transcriptomic Analysis of Trichoderma atroviride Overgrowing Plant-Wilting Verticillium dahliae Reveals the Role of a New M14 Metallocarboxypeptidase CPA1 in Biocontrol
- PMID: 31191472
- PMCID: PMC6545926
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01120
Transcriptomic Analysis of Trichoderma atroviride Overgrowing Plant-Wilting Verticillium dahliae Reveals the Role of a New M14 Metallocarboxypeptidase CPA1 in Biocontrol
Abstract
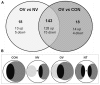
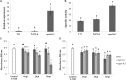
Verticillium dahliae, a vascular-colonizing fungus, causes economically important wilt diseases in many crops, including olive trees. Trichoderma spp. have demonstrated an effective contribution as biocontrol agents against this pathogen through a variety of mechanisms that may involve direct mycoparasitism and antibiosis. However, molecular aspects underlaying Trichoderma-V. dahliae interactions are not well known yet due to the few studies in which this pathogen has been used as a target for Trichoderma. In the present study, Trichoderma atroviride T11 overgrew colonies of V. dahliae on agar plates and inhibited growth of highly virulent defoliating (D) V. dahliae V-138I through diffusible molecules and volatile organic compounds produced before contact. A Trichoderma microarray approach of T11 growing alone (CON), and before contact (NV) or overgrowing (OV) colonies of V-138I, helped to identify 143 genes that differed significantly in their expression level by more than twofold between OV and CON or NV. Functional annotation of these genes indicated a marked up-regulation of hydrolytic, catalytic and transporter activities, and secondary metabolic processes when T11 overgrew V-138I. This transcriptomic analysis identified peptidases as enzymatic activity overrepresented in the OV condition, and the cpa1 gene encoding a putative carboxypeptidase (ID number 301733) was selected to validate this study. The role of cpa1 in strain T11 on antagonism of V-138I was analyzed by a cpa1-overexpression approach. The increased levels of cpa1 expression and protease activity in the cpa1-overexpressed transformants compared to those in wild-type or transformation control strains were followed by significantly higher antifungal activity against V-138I in in vitro assays. The use of Trichoderma spp. for the integrated management of plant diseases caused by V. dahliae requires a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying this interaction that might provide an increase on its efficiency.
Keywords: Verticillium wilt; carboxypeptidase; cpa1-overexpressed mutants; microarray; mycoparasitism; secondary metabolism.
Figures

References
-
- Cardoza R. E., Vizcaíno J. A., Hermosa M. R., Sousa S., González F. J., Llobell A., et al. (2006). Cloning and characterization of the erg1 gene of Trichoderma harzianum: effect of the erg1 silencing on ergosterol biosynthesis and resistance to terbinafine. Fungal Genet. Biol. 43 269–283. - PubMed
-
- Carrero-Carrón I., Trapero-Casas J. L., Olivares-García C., Monte E., Hermosa R., Jiménez-Díaz R. M. (2016). Trichoderma asperellum is effective for biocontrol of Verticillium wilt in olive caused by the defoliating pathotype of Verticillium dahliae. Crop Prot. 88 45–52. 10.1016/j.cropro.2016.05.009 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

