Detection and Genomic Characterization of a Morganella morganii Isolate From China That Produces NDM-5
- PMID: 31191484
- PMCID: PMC6546717
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01156
Detection and Genomic Characterization of a Morganella morganii Isolate From China That Produces NDM-5
Abstract
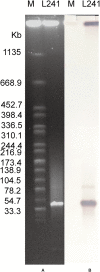
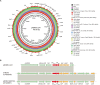
The increasing prevalence and transmission of the carbapenem resistance gene bla NDM-5 has led to a severe threat to public health. So far, bla NDM-5 has been widely detected in various species of Enterobacterales and different hosts across various cities. However, there is no report on the bla NDM-5- harboring Morganella morganii. In January 2016, the first NDM-5-producing Morganella morganii L241 was found in a stool sample of a patient diagnosed as recurrence of liver cancer in China. Identification of the species was performed using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Carbapenemase genes were identified through both PCR and sequencing. To investigate the characteristics and complete genome sequence of the bla NDM-5-harboring clinical isolate, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, S1 nuclease pulsed field gel electrophoresis, Southern blotting, transconjugation experiment, complete genome sequencing, and comparative genomic analysis were performed. M. morganii L241 was found to be resistant to broad-spectrum cephalosporins and carbapenems. The complete genome of L241 is made up from both a 3,850,444 bp circular chromosome and a 46,161 bp self-transmissible IncX3 plasmid encoding bla NDM-5, which shared a conserved genetic context of bla NDM-5 (ΔIS3000-ΔISAba125-IS5-bla NDM-5-ble-trpF-dsbC-IS26). BLASTn analysis showed that IncX3 plasmids harboring bla NDM genes have been found in 15 species among Enterobacterales from 13 different countries around the world thus far. In addition, comparative genomic analysis showed that M. morganii L241 exhibits a close relationship to M. morganii subsp. morganii KT with 107 SNPs. Our research demonstrated that IncX3 is a key element in the worldwide dissemination of bla NDM-5 among various species. Further research will be necessary to control and prevent the spread of such plasmids.
Keywords: IncX3; Morganella morganii; blaNDM–5; comparative genomic analysis; complete genome sequence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emergence of a Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolate Co-harbouring Dual bla NDM- 6 -Carrying Plasmids in China.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 18;13:900831. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.900831. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35663874 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemic IncX3 plasmids spreading carbapenemase genes in the United Arab Emirates and worldwide.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Jun 21;12:1729-1742. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S210554. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31417290 Free PMC article.
-
Further Spread of bla NDM-5 in Enterobacteriaceae via IncX3 Plasmids in Shanghai, China.Front Microbiol. 2016 Mar 30;7:424. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00424. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27065982 Free PMC article.
-
Dissemination of the blaNDM-5 Gene via IncX3-Type Plasmid among Enterobacteriaceae in Children.mSphere. 2020 Jan 8;5(1):e00699-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00699-19. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 31915216 Free PMC article.
-
High Prevalence of Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacter cloacae From Three Tertiary Hospitals in China.Front Microbiol. 2019 Aug 9;10:1610. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01610. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31447788 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Emergence of NDM-5 Producing Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella aerogenes in a Pediatric Hospital in Shanghai, China.Front Public Health. 2021 Feb 25;9:621527. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.621527. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33718321 Free PMC article.
-
Carbapenem-resistant Morganella morganii carrying blaKPC-2 or blaNDM-1 in the clinic: one-decade genomic epidemiology analysis.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Apr;13(4):e0247624. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02476-24. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40029330 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of bla NDM-5-carrying plasmids in two clinical Salmonella isolates from Jiaxing city, China.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1620907. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1620907. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40641878 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing and Characterization of M. morganii Strain UM869: A Comprehensive Comparative Genomic Analysis of Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance, and Functional Pathways.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 16;14(6):1279. doi: 10.3390/genes14061279. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372459 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Characteristic of NDM-5-Producing Klebsiella Quasipneumoniae and Klebsiella Pneumoniae in China.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Feb 7;18:769-774. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S492203. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 39936038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad N., Ali S. M., Khan A. U. (2018). Detection of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase variants NDM-4, NDM-5, and NDM-7 in Enterobacter aerogenes isolated from a neonatal intensive care unit of a north india hospital: a first report. Microb. Drug Resist. 24 161–165. 10.1089/mdr.2017.0038 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cerdeira L. T., Cunha M. P. V., Francisco G. R., Bueno M. F. C., Araujo B. F., Ribas R. M., et al. (2017). IncX3 plasmid harboring a non-Tn4401 genetic element (NTEKPC) in a hospital-associated clone of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST340/CG258. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 89 164–167. 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2017.06.022 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

