Three Capsular Polysaccharide Synthesis-Related Glucosyltransferases, GT-1, GT-2 and WcaJ, Are Associated With Virulence and Phage Sensitivity of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 31191500
- PMCID: PMC6546894
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01189
Three Capsular Polysaccharide Synthesis-Related Glucosyltransferases, GT-1, GT-2 and WcaJ, Are Associated With Virulence and Phage Sensitivity of Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
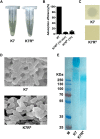
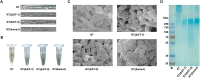
Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) spp. are important nosocomial and community-acquired opportunistic pathogens, which cause various infections. We observed that K. pneumoniae strain K7 abruptly mutates to rough-type phage-resistant phenotype upon treatment with phage GH-K3. In the present study, the rough-type phage-resistant mutant named K7RR showed much lower virulence than K7. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS-MS) analysis indicated that WcaJ and two undefined glycosyltransferases (GTs)- named GT-1, GT-2- were found to be down-regulated drastically in K7RR as compared to K7 strain. GT-1, GT-2, and wcaJ are all located in the gene cluster of capsular polysaccharide (CPS). Upon deletion, even of single component, of GT-1, GT-2, and wcaJ resulted clearly in significant decline of CPS synthesis with concomitant development of GH-K3 resistance and decline of virulence of K. pneumoniae, indicating that all these three GTs are more likely involved in maintenance of phage sensitivity and bacterial virulence. Additionally, K7RR and GT-deficient strains were found sensitive to endocytosis of macrophages. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway of macrophages was significantly activated by K7RR and GT-deficient strains comparing with that of K7. Interestingly, in the presence of macromolecular CPS residues (>250 KD), K7(ΔGT-1) and K7(ΔwcaJ) could still be bounded by GH-K3, though with a modest adsorption efficiency, and showed minor virulence, suggesting that the CPS residues accumulated upon deletion of GT-1 or wcaJ did retain phage binding sites as well maintain mild virulence. In brief, our study defines, for the first time, the potential roles of GT-1, GT-2, and WcaJ in K. pneumoniae in bacterial virulence and generation of rough-type mutation under the pressure of bacteriophage.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; WcaJ; glucosyltransferase (GT); phage resistance; virulence.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Smooth-Type, Phage-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Mutant Strain Reveals that OmpC Is Indispensable for Infection by Phage GH-K3.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Oct 17;84(21):e01585-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01585-18. Print 2018 Nov 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30171001 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae to Phage hvKpP3 Due to High-Molecular Weight Lipopolysaccharide Synthesis Failure.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0438422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04384-22. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37022197 Free PMC article.
-
Different regulatory mechanisms of the capsule in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumonia: "direct" wcaJ variation vs. "indirect" rmpA regulation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Apr 25;13:1108818. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1108818. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37180440 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of the glycosyltransferase WcaJ in Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC13883 affects biofilm formation, increases polymyxin resistance and reduces murine macrophage activation.Microbiology (Reading). 2019 Aug;165(8):891-904. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000827. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Microbiology (Reading). 2019. PMID: 31246167
-
A Frameshift Mutation in wcaJ Associated with Phage Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae.Microorganisms. 2020 Mar 7;8(3):378. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8030378. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32156053 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Phage resistance mutations affecting the bacterial cell surface increase susceptibility to fungi in a model cheese community.ISME Commun. 2024 Aug 2;4(1):ycae101. doi: 10.1093/ismeco/ycae101. eCollection 2024 Jan. ISME Commun. 2024. PMID: 39296780 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Changes and Genetic Divergence of Vibrio alginolyticus Under Phage Infection Stress Revealed by Whole-Genome Sequencing and Resequencing.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 4;12:710262. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.710262. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34671325 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of polysaccharides production using microparticle enhanced technology by Paraisaria dubia.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Jan 28;21(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01733-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 35090444 Free PMC article.
-
Growth stage-related capsular polysaccharide translocon Wza in Vibrio splendidus modifies phage vB_VspM_VS2 susceptibility.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 16;7(1):1338. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07038-z. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39414953 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 Isolates and Their Interactions with Lytic Phages.Viruses. 2019 Nov 19;11(11):1080. doi: 10.3390/v11111080. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31752386 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

