Antimicrobial Profiling of Bacteria Isolated from Fish Sold at Informal Market in Mufakose, Zimbabwe
- PMID: 31191658
- PMCID: PMC6525903
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8759636
Antimicrobial Profiling of Bacteria Isolated from Fish Sold at Informal Market in Mufakose, Zimbabwe
Abstract
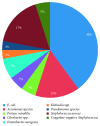
The number of infections caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria is rising worldwide. Fish from multisource pollution waters can harbour multidrug-resistant bacteria that can be disseminated to humans through eating or contact of contaminated fish. A cross-sectional study was carried out to (i) isolate and phenotypically identify bacteria from 36 fish samples from informal market in Mufakose, Harare, and (ii) determine the antibiotic sensitivity pattern of the isolated bacteria against ten available antibiotics (ampicillin 10 μg, gentamycin 30 μg, penicillin G 10 μg, erythromycin 15 μg, tetracycline 30 μg, kanamycin 30 μg, neomycin 10 μg, cloxacillin 5 μg, lincomycin 15 μg, and sulfamethoxazole 25 μg) using the Kirby-Bauer disk agar diffusion method. Eight bacterial genera were isolated and identified, and they were Escherichia, Aeromonas, Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas, Citrobacter, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Proteus. Among the isolates, Escherichia coli was isolated most frequently (44%) followed by Staphylococcus aureus (19%), Enterobacter aerogenes (7%), Aeromonas spp. (5%), Proteus mirabilis (5%), Citrobacter (5%), and coagulase-negative Staphylococci (5%) and the least frequent were Klebsiella (3%) and Pseudomonas (3%). All isolates were susceptible to gentamycin. Varying antibiotic resistance rates were observed to lincomycin (100%), ampicillin (81%), penicillin (67%), erythromycin (65%), tetracycline (63%), neomycin (61%), cloxacillin (43%), kanamycin (24%), and sulphamethoxazole (13%). All the isolates were multidrug-resistant (resistant to at 3 or more drugs tested) except Proteus mirabilis. Proteus mirabilis has multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) index of 0.2, and the other isolated bacteria had MAR indexes greater than 0.2 ranging from 0.3 to 0.7. Those MAR indexes above 0.2 showed that the bacteria isolates are from a high risk source where antibiotics were frequently used, possibly from sewage effluents. Isolation of enteric bacteria such as Escherichia coli is an indication of faecal contamination, and this poses a high risk to animal and human health. These significant findings call for effective risk assessment models and management plans that protect human, animal, and environmental health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of bacterial foodborne pathogens in Nile tilapia fish (Oreochromis niloticus) at points of retail sale in Nairobi, Kenya.Front Antibiot. 2023 May 24;2:1156258. doi: 10.3389/frabi.2023.1156258. eCollection 2023. Front Antibiot. 2023. PMID: 39816642 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic bacteria isolated from blood cultures of patients and their antibiotic susceptibilities in Harare, Zimbabwe.Cent Afr J Med. 1996 Dec;42(12):332-6. Cent Afr J Med. 1996. PMID: 9164012
-
Antimicrobial resistance patterns of clinical bacterial isolates in southwestern Ethiopia.Ethiop Med J. 2007 Oct;45(4):363-70. Ethiop Med J. 2007. PMID: 18326346
-
[Antibiotic sensitivity to isolated bacteria in pediatric urinary tract infections].Arch Pediatr. 1998;5 Suppl 3:266S-268S. doi: 10.1016/s0929-693x(98)80146-2. Arch Pediatr. 1998. PMID: 9759315 Review. French.
-
[Current status of antibiotic therapy].Z Gesamte Inn Med. 1973 Feb 15;28(4):85-92. Z Gesamte Inn Med. 1973. PMID: 4349582 Review. German. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Bioactivity of Essential Oils for Mitigation of Listeria monocytogenes Isolated from Fresh Retail Chicken Meat.Foods. 2021 Dec 4;10(12):3006. doi: 10.3390/foods10123006. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34945555 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence, antimicrobial resistance and phylogenetic analysis of zoonotic walking pneumonia Mycoplasma arginini in the one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius).Acta Trop. 2020 Jul;207:105500. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105500. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Acta Trop. 2020. PMID: 32330451 Free PMC article.
-
Functional properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Ivory Coast.BMC Microbiol. 2023 May 25;23(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02899-6. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37231432 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Antibiotic Resistance-Coliform Bacteria in Some Selected Fish Farms of the Central Region of Ghana.Scientifica (Cairo). 2020 Dec 4;2020:6641461. doi: 10.1155/2020/6641461. eCollection 2020. Scientifica (Cairo). 2020. PMID: 33376622 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteria of Zoonotic Interest Identified on Edible Freshwater Fish Imported to Australia.Foods. 2023 Mar 17;12(6):1288. doi: 10.3390/foods12061288. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36981215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FAO. Social issues in small-scale fisheries: how a human rights perspective can contribute to respective fisheries. Proceedings of the Presentation to FAO Committee of Fisheries No 27; March 2007; Rome, Italy.
-
- Allison E. H., Perry A. L., Badjeck M.-C., et al. Vulnerability of national economies to the impacts of climate change on fisheries. Fish and Fisheries. 2009;10(2):173–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2979.2008.00310.x. - DOI
-
- Manhondo P., Gono R. K., Muzondiwa J., Mafa B. Isolation and identification of pathogenic bacteria in edible fish: a case study of bacterial resistance to antibiotics at Lake Chivero, Zimbabwe. African Journal of Agricultural Research. 2018 In press.
-
- Sichewo P. R., Gono R. K., Muzondiwa J., Mungwadzi W. Isolation and identification of pathogenic bacteria in edible fish: a case study of rural aquaculture projects feeding livestock manure to fish in Zimbabwe. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences. 2014;3(11):897–904.
-
- Rastogi S. C. Essentials of Animal Physiology. 4th. New Delhi: New Age International Limited; 2007.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous