Autoimmune pancreatitis with spontaneous remission on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- PMID: 31191774
- PMCID: PMC6545417
- DOI: 10.2185/jrm.2974
Autoimmune pancreatitis with spontaneous remission on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography
Abstract
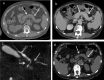
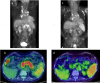
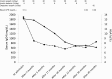
A 79-year-old man with elevated blood glucose was started on insulin therapy. IgG4 was as high as 1,830 mg/dL, and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) confirmed diffuse pancreatic enlargement and accumulation of FDG. Based on the above, autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) was diagnosed, but steroid treatment was not performed. IgG4 later declined, and FDG accumulation in the pancreas disappeared on FDG-PET/CT at the age of 83 years. AIP was thought to have gradually remitted spontaneously over time. FDG-PET/CT is useful for evaluating AIP activity.
Keywords: FDG-PET/CT; IgG4; autoimmune pancreatitis; diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ministry of Health Labor and Welfare Investigative Research Group for Refractory Pancreatic Disease•Japan Pancreas Society, Autoimmune Pancreatitis Clinical Practice Guideline 2013 Pancreas 2013; 28: 717–783 (in Japanese).

