The calcium-dependent lipopeptide antibiotics: structure, mechanism, & medicinal chemistry
- PMID: 31191855
- PMCID: PMC6533798
- DOI: 10.1039/c9md00126c
The calcium-dependent lipopeptide antibiotics: structure, mechanism, & medicinal chemistry
Abstract
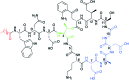
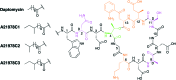
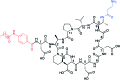
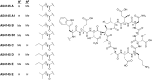
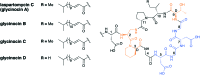
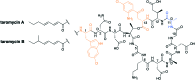
To push back the growing tide of antibacterial resistance the discovery and development of new antibiotics is a must. In recent years the calcium-dependent lipopeptide antibiotics (CDAs) have emerged as a potential source of new antibacterial agents rich in structural and mechanistic diversity. All CDAs share a common lipidated cyclic peptide motif containing amino acid side chains that specifically chelate calcium. It is only in the calcium bound state that the CDAs achieve their potent antibacterial activities. Interestingly, despite their common structural features, the mechanisms by which different CDAs target bacteria can vary dramatically. This review provides both a historic context for the CDAs while also addressing the state of the art with regards to their discovery, optimization, and antibacterial mechanisms.
Figures









References
-
- O'Neill J., Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations, 2014, http://www.jpiamr.eu/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/AMR-Review-Paper-Tacklin....
-
- CDCD, US Dep. Heal. Hum. Serv.
-
- Wang Y., Zhang R., Li J., Wu Z., Yin W., Schwarz S., Tyrrell J. M., Zheng Y., Wang S., Shen Z., Liu Z., Liu J., Lei L., Li M., Zhang Q., Wu C., Zhang Q., Wu Y., Walsh T. R., Shen J. Nat. Microbiol. 2017;2:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

