Selective modulation of the cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptor as an emerging platform for the treatment of neuropathic pain
- PMID: 31191856
- PMCID: PMC6533890
- DOI: 10.1039/c8md00595h
Selective modulation of the cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptor as an emerging platform for the treatment of neuropathic pain
Abstract
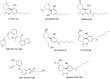
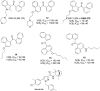
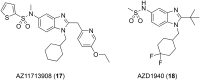
Neuropathic pain is caused by a lesion or dysfunction in the nervous system, and it may arise from illness, be drug-induced or caused by toxin exposure. Since the discovery of two G-protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) nearly three decades ago, there has been a rapid expansion in our understanding of cannabinoid pharmacology. This is currently one of the most active fields of neuropharmacology, and interest has emerged in developing cannabinoids and other small molecule modulators of CB1 and CB2 as therapeutics for neuropathic pain. This short review article provides an overview of the chemotypes currently under investigation for the development of novel neuropathic pain treatments targeting CB1 receptors.
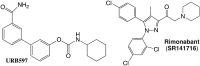
Figures
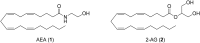
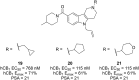
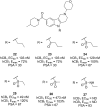

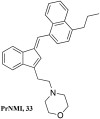

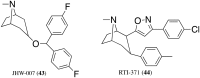
Similar articles
-
The pharmacology of cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: an overview.Int J Obes (Lond). 2006 Apr;30 Suppl 1:S13-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803272. Int J Obes (Lond). 2006. PMID: 16570099 Review.
-
Mastering tricyclic ring systems for desirable functional cannabinoid activity.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Nov;69:881-907. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.09.038. Epub 2013 Sep 29. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24125850 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic cannabinoid administration blocks the development of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic nociception during analgesic treatment and following cessation of drug delivery.Mol Pain. 2014 Apr 18;10:27. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-10-27. Mol Pain. 2014. PMID: 24742127 Free PMC article.
-
Classical cannabinoid receptors as target in cancer-induced bone pain: a systematic review, meta-analysis and bioinformatics validation.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 9;14(1):5782. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56220-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38461339 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological actions of cannabinoids.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2005;(168):1-51. doi: 10.1007/3-540-26573-2_1. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16596770 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-canonical Molecular Targets for Novel Analgesics: Intracellular Calcium and HCN Channels.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(11):1937-1951. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210119153047. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33463473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiallodynic effect of PhAR-DBH-Me involves cannabinoid and TRPV1 receptors.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020 Oct;8(5):e00663. doi: 10.1002/prp2.663. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020. PMID: 32965798 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Dynamics of the Structural States of Cannabinoid Receptors and the Role of Different Modulators.Life (Basel). 2022 Dec 18;12(12):2137. doi: 10.3390/life12122137. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556502 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based identification of a G protein-biased allosteric modulator of cannabinoid receptor CB1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jun 11;121(24):e2321532121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2321532121. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38830102 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual library docking for cannabinoid-1 receptor agonists with reduced side effects.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 6;16(1):2237. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57136-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40044644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Treede R.-D., Jensen T. S., Campbell J. N., Cruccu G., Dostrovsky J. O., Griffin J. W., Hansson P., Hughes R., Nurmikko T., Serra J. Neurology. 2007;70:1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Jensen T. S., Baron R., Haanpaa M., Kalso E., Loeser J. D., Rice A. S., Treede R.-D. Pain. 2011;152:2204–2205. - PubMed
-
- Treede R.-D., Rief W., Barke A., Aziz Q., Bennett M. I., Benoliel R., Cohen M., Evers S., Finnerup N. B., First M. B., Giamberardino M. A., Kaasa S., Kosek E., Lavand'homme P., Nicholas M., Perrot S., Scholz J., Schug S., Smith B. H., Svensson P., Vlaeyen J. W., Wang S.-J. Pain. 2015;156:1003–1007. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Woolf C. J., Mannion R. J. Lancet. 1999;353:1959–1964. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

