New methods to assess 6-thiopurine toxicity and expanding its therapeutic application to pancreatic cancer via small molecule potentiators
- PMID: 31191862
- PMCID: PMC6533796
- DOI: 10.1039/c9md00010k
New methods to assess 6-thiopurine toxicity and expanding its therapeutic application to pancreatic cancer via small molecule potentiators
Abstract
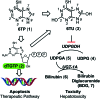
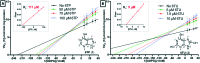
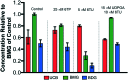
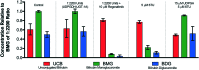
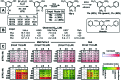
6-Thiopurine (6TP) is a potent cytotoxic agent that is a clinically prescribed anti-metabolite employed in the treatment of numerous blood cancers since 1952. However, its reported severe toxicities limit its general usage in the clinic. We previously have undertaken investigations into identifying the mode of toxicity for 6TP, and have found that the oxidative metabolites of 6TP, specifically 6-thiouric acid (6TU), is responsible for the in vitro inhibition of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase (UDPGDH) in a UV-vis method. In this method, inhibition was quantified through the quantification of NADH production, however, purines absorb at the same wavelength and thereby can interfere with the NADH detection. Herein, we report a HPLC method that allows for direct quantification of UDP-glucuronic acid, product from UDPGDH, for the assessment of inhibition towards UDPGDH with no interference from purines. In this method it was revealed that 6TP possesses a greater inhibitory properties than previously observed; 111 vs. 288 μM. Building upon the data collected from a previously performed rat hepatocyte study, which correlated our in vitro to in vivo inhibition theories about UDPGDH, we have developed a bio-mimic in vitro assay to aid in the inhibitory assessment of 6TP and analogs. In our efforts to expand the use of 6TP, and analogs constructed, our laboratory has undertaken a screening campaign to identify small molecule potentiators that work in synergy with 6TP in other types of cancers. Three chalcone-based compounds have been discovered through our total synthesis campaign of uvaretin, and it has been found that 11c has strong synergism with 6TP in the pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2. Through the work presented herein, we reveal new methods to assess toxicity of 6TP and future analogs and new small molecules that work in synergy to expand the therapeutic applications of this neglected cytotoxic agent.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

