The nuclear export inhibitor aminoratjadone is a potent effector in extracellular-targeted drug conjugates
- PMID: 31191875
- PMCID: PMC6540907
- DOI: 10.1039/c8sc05542d
The nuclear export inhibitor aminoratjadone is a potent effector in extracellular-targeted drug conjugates
Abstract
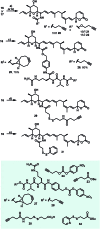
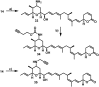
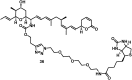
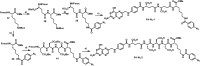
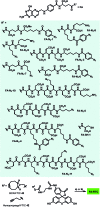
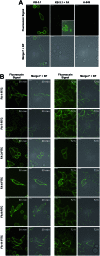
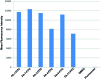
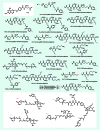
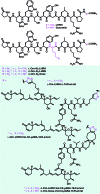
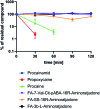
The concept of targeted drug conjugates has been successfully translated to clinical practice in oncology. Whereas the majority of cytotoxic effectors in drug conjugates are directed against either DNA or tubulin, our study aimed to validate nuclear export inhibition as a novel effector principle in drug conjugates. For this purpose, a semisynthetic route starting from the natural product ratjadone A, a potent nuclear export inhibitor, has been developed. The biological evaluation of ratjadones functionalized at the 16-position revealed that oxo- and amino-analogues had very high potencies against cancer cell lines (e.g. 16R-aminoratjadone 16 with IC50 = 260 pM against MCF-7 cells, or 19-oxoratjadone 14 with IC50 = 100 pM against A-549 cells). Mechanistically, the conjugates retained a nuclear export inhibitory activity through binding CRM1. To demonstrate a proof-of-principle for cellular targeting, folate- and luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH)-based carrier molecules were synthesized and coupled to aminoratjadones as well as fluorescein for cellular efficacy and imaging studies, respectively. The Trojan-Horse conjugates selectively addressed receptor-positive cell lines and were highly potent inhibitors of their proliferation. For example, the folate conjugate FA-7-Val-Cit-pABA-16R-aminoratjadone had an IC50 of 34.3 nM, and the LHRH conjugate d-Orn-Gose-Val-Cit-pABA-16R-aminoratjadone had an IC50 of 12.8 nM. The results demonstrate that nuclear export inhibition is a promising mode-of-action for extracellular-targeted drug conjugate payloads.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of Aminoratjadone Derivatives as Potent Noncovalent CRM1 Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2023 Sep 14;66(17):11940-11950. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00549. Epub 2023 Aug 18. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37595020
-
Synthesis and Preclinical Evaluation of Indole Triazole Conjugates as Microtubule Targeting Agents that are Effective against MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(8):1047-1055. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200925102940. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32981511
-
Ratjadones inhibit nuclear export by blocking CRM1/exportin 1.Exp Cell Res. 2003 Jun 10;286(2):321-31. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00100-9. Exp Cell Res. 2003. PMID: 12749860
-
Targeting cytotoxic conjugates of somatostatin, luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and bombesin to cancers expressing their receptors: a "smarter" chemotherapy.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(9):1167-80. doi: 10.2174/1381612053507594. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. PMID: 15853664 Review.
-
Inhibition of CRM1-dependent nuclear export sensitizes malignant cells to cytotoxic and targeted agents.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Aug;27:62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24631834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Pseudoglucosinolates Releasing Isothiocyanates in the Presence of Azoreductases.Chembiochem. 2025 Jun 16;26(12):e202500152. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202500152. Epub 2025 May 29. Chembiochem. 2025. PMID: 40345969 Free PMC article.
-
Masked Amino Trimethyl Lock (H2 N-TML) Systems: New Molecular Entities for the Development of Turn-On Fluorophores and Their Application in Hydrogen Sulfide (H2 S) Imaging in Human Cells.Chemistry. 2022 Jan 10;28(2):e202103525. doi: 10.1002/chem.202103525. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Chemistry. 2022. PMID: 34713944 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme-Responsive Nanoparticles and Coatings Made from Alginate/Peptide Ciprofloxacin Conjugates as Drug Release System.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 May 29;10(6):653. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10060653. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072352 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of nucleo‑cytoplasmic transport factor exportin 1 in malignancy (Review).Med Int (Lond). 2021 Dec 28;2(1):2. doi: 10.3892/mi.2021.27. eCollection 2022 Jan-Feb. Med Int (Lond). 2021. PMID: 38938904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

