Development and reliability of a hand-held dynamometer device to measure the ankle dorsiflexor muscle strength
- PMID: 31191956
- PMCID: PMC6531795
- DOI: 10.1177/2055668318802558
Development and reliability of a hand-held dynamometer device to measure the ankle dorsiflexor muscle strength
Abstract
Background: Ankle dorsiflexor muscle strength is a crucial component of gait.
Objective: We describe the development of a simple, hand-held dynamometer to measure the ankle dorsiflexor muscle strength in the sitting position. In addition, we examine its intra- and inter-rater reliability.
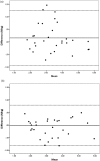
Methods: Measurements of the peak ankle dorsiflexor muscle strength were obtained by two examiners for 30 ankles of 15 healthy adults at two time points, with a one-day interval between measurements, to determine the inter- and intra-rater reliability. The intraclass correlation coefficients were calculated, and an intraclass correlation coefficient > 0.90 was considered as excellent reliability. A Bland-Altman analysis was used to assess systemic bias. The minimal detectable change in muscle strength was calculated with a confidence level of 95% (MDC95).
Results: The reliability of the device was excellent for both intra- (intraclass correlation coefficients [1,3] = 0.94) and inter-rater (intraclass correlation coefficients [2,3] = 0.96) comparisons. No fixed or proportional bias was observed between the two examiners. The MDC95 was 0.77 N/kg.
Conclusions: Our results indicate the excellent reliability and responsiveness of our device. By obtaining the measurements of dorsiflexor strength while sitting, compensatory motions are suppressed, yielding a more consistent measurement that can be reliably used to detect subtle changes in the ankle dorsiflexor muscle strength.
Keywords: Ankle dorsiflexor muscle strength; compensatory motion; hand-held dynamometer; inter-rater; intra-rater; reliability testing.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Minimal Detectable Change in Muscle Strength Measurements Obtained Using a Hand-Held Dynamometer in Patients with Stroke.Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci. 2025 Apr 17;16:9-18. doi: 10.11336/jjcrs.16.9. eCollection 2025. Jpn J Compr Rehabil Sci. 2025. PMID: 40276357 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of a handheld myotonometer measuring myofascial stiffness of lower lumbar myofascial tissue in healthy adults.PeerJ. 2024 Nov 18;12:e18524. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18524. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39575173 Free PMC article.
-
The Intra- and Inter-Rater Reliability of a Variety of Testing Methods to Measure Shoulder Range of Motion, Hand-behind-Back and External Rotation Strength in Healthy Participants.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 4;19(21):14442. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192114442. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36361321 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric properties of a standardized protocol of muscle strength assessment by hand-held dynamometry in healthy adults: a reliability study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Apr 14;24(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06400-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37060020 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Lower Limb Muscle Strength and Power Using Hand-Held and Fixed Dynamometry: A Reliability and Validity Study.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 28;10(10):e0140822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140822. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26509265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burns J, Ryan MM, Ouvrier RA. Evolution of foot and ankle manifestations in children with CMT1A. Muscle Nerve 2009; 39: 158–166. - PubMed
-
- Ng SS, Hui-Chan CW. Ankle dorsiflexor, not plantarflexor strength, predicts the functional mobility of people with spastic hemiplegia. J Rehabil Med 2013; 45: 541–545. - PubMed
-
- Bohannon RW. Test-retest reliability of hand-held dynamometry during a single session of strength assessment. Phys Ther 1986; 66: 206–209. - PubMed
-
- Bohannon RW. Reference values for extremity muscle strength obtained by hand-held dynamometry from adults aged 20 to 79 years. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1997; 78: 26–32. - PubMed
-
- Wang CY, Olson SL, Protas EJ. Test-retest strength reliability: hand-held dynamometry in community-dwelling elderly fallers. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2002; 83: 811–815. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources