Investigation of Blood Characteristics in Nonsyndromic Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 31191992
- PMCID: PMC6525908
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/1902915
Investigation of Blood Characteristics in Nonsyndromic Retinitis Pigmentosa: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the characteristics of blood in nonsyndromic retinitis pigmentosa (RP) and reveal the pathogenesis of blood cells involved in blood stasis in RP.
Design: This is a retrospective observational study.
Methods: We collected vein blood from 101 cases of patients with nonsyndromic RP and 120 cases of normal individuals according to a single-blind study and used routine clinical examination to detect the indicators of blood. All the subjects were mainly from the central south of China. Data were analyzed statistically between the RP group and normal control.
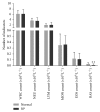
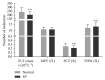
Results: The indicator of platelet distribution width (PDW) in patients with RP was higher than that in the normal group; the indicators of red blood cell (RBCs), hemoglobin (HGB), hematocrit (HCT), basophils (BASs), platelets (PLTs), and plateletcrit (PCT) in the RP group were lower than those in the normal control. The differences were statistically very significant between the RP group and normal group (p < 0.01). There were no statistical differences in the other indicators between the RP and normal group.
Conclusions: The changes in RBCs and PLTs in patients with RP implied that RP induces RBC aggregation and platelet activation, leading to blood stasis which in turn initiates more apoptosis.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

