Zinc and Iron Homeostasis: Target-Based Drug Screening as New Route for Antifungal Drug Development
- PMID: 31192169
- PMCID: PMC6548825
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00181
Zinc and Iron Homeostasis: Target-Based Drug Screening as New Route for Antifungal Drug Development
Abstract
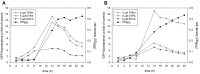
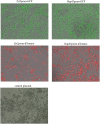
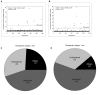
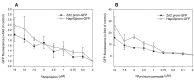
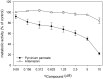
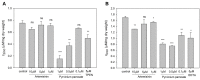
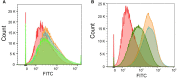
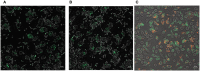
The incidence of fungal diseases is on the rise and the number of fatalities is still unacceptably high. While advances into antifungal drug development have been made there remains an urgent need to develop novel antifungal agents targeting as-yet unexploited pathways, such as metal ion homeostasis. Here we report such an approach by developing a metal sensor screen in the opportunistic human fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Using this reporter strain, we screened a library of 1,200 compounds and discovered several active compounds not previously described as chemical entities with antifungal properties. Two of these, artemisinin and pyrvinium pamoate, have been further characterized and their interference with metal homeostasis and potential as novel antifungal compounds validated. Lastly, we demonstrate that the same strain can be used to report on intracellular conditions within host phagocytes, paving the way toward the development of novel screening platforms that could identify compounds with the potential to perturb ion homeostasis of the pathogen specifically within host cells.
Keywords: Candida; antifungals; artemisinin; high throughput drug screening; iron homeostasis; pyrvinium pamoate; zinc homeostasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A chemical screen identifies structurally diverse metal chelators with activity against the fungal pathogen Candida albicans.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Apr 2;12(4):e0409523. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04095-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38376363 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Anti-Virulence Approaches for Candidiasis via a Novel Series of Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Candida albicans Filamentation.mBio. 2017 Dec 5;8(6):e01991-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01991-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 29208749 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Metal Chelation by a Thiosemicarbazone Derivative Interferes with Mitochondrial Respiration and Ribosome Biogenesis in Candida albicans.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0195121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01951-21. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35412374 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing Metal Homeostasis Offers Novel and Promising Targets Against Candida albicans.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2020;17(4):415-429. doi: 10.2174/1570163816666190227231437. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2020. PMID: 30827249 Review.
-
Promising Antifungal Targets Against Candida albicans Based on Ion Homeostasis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Sep 4;8:286. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00286. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30234023 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nutritional immunity: targeting fungal zinc homeostasis.Heliyon. 2021 Aug 16;7(8):e07805. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07805. eCollection 2021 Aug. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34466697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antifungal Drug Repurposing.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Nov 15;9(11):812. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9110812. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33203147 Free PMC article.
-
Calcitermin-Loaded Smart Gels Activity against Candida albicans: A Preliminary In Vitro Study.Gels. 2023 Feb 18;9(2):165. doi: 10.3390/gels9020165. Gels. 2023. PMID: 36826335 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrvinium pamoate regulates MGMT expression through suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to enhance the glioblastoma sensitivity to temozolomide.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Oct 12;7(1):288. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00654-2. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34642308 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Profiling of the Candida auris Response to Exogenous Farnesol Exposure.mSphere. 2021 Oct 27;6(5):e0071021. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00710-21. Epub 2021 Oct 13. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34643421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernardo S. M., Allen C. P., Waller A., Young S. M., Oprea T., Sklar L. A., et al. . (2014). An automated high-throughput cell-based multiplexed flow cytometry assay to identify novel compounds to target Candida albicans virulence-related proteins. PLoS ONE 9:e110354. 10.1371/journal.pone.0110354 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Casalinuovo I. A., Sorge R., Bonelli G., Di Francesco P. (2017). Evaluation of the antifungal effect of EDTA, a metal chelator agent, on Candida albicans biofilm. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 21, 1413–1420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

