Impact of tumor cytoreduction in metastatic prostate cancer
- PMID: 31192170
- PMCID: PMC6511624
- DOI: 10.2147/RRU.S204507
Impact of tumor cytoreduction in metastatic prostate cancer
Abstract
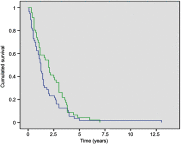
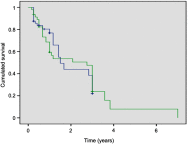
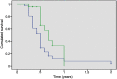
Objective: To assess the impact of tumor cytoreduction on cancer outcomes and patient survival in metastatic prostate cancer. Patients and methods: It is a prospective study spanning a two-year period between October 1st 2015 and March 31st 2017. We enrolled 102 cases of metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Fifty-seven (57) patients had exclusively androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) (group 1) and 45 had, in addition, an open prostatectomy or Transurethral resection of the Prostate (group 2). We compared both groups using the total PSA nadir, the time to PSA nadir, the overall survival (OS), and the progression-free survival (PFS). Results: The average nadir PSA was lower for the tumor cytoreduction group (16.8±1.6 ng/mL (0.01-193.5) versus 110.7±17.9 ng/mL (0.01-1379)). Median time to PSA nadir was shorter in patients in the ADT only group (8 months vs 3 months (p=0.025)). The OS was shorter in patients treated with ADT only compared to the tumor cytoreduction group (median 14 months vs 24 months, respectively (p=0.03)). Similarly, tumor cytoreduction had a positive impact on patient progression (median PFS 20 months (group 1) vs 43 months (group 2)). Conclusion: Tumor cytoreduction has a positive impact on the oncological results and the survival of patients under ADT.
Keywords: TURP; androgen suppression; cytoreduction; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Fall B, Tengue K, Sow Y, et al. Place of bilateral pulpectomy as a method of androgen suppression therapy in prostate cancer. Prog Urol. 2012;17(6):1027–3. - PubMed
-
- Qin X-J, Ma C-G, Ye D-W, et al. Tumor cytoreduction results in better response to androgen ablation: a preliminary report of palliative transurethral resection of the prostate in metastatic hormone sensitive prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. 2012;30:145–149. doi:10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.02.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huggins C, Hodges CV. Studies on prostatic cancer. I. The effect of castration, of estrogen and of androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer Res. 1941;1:293–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

