Molecular Characterization of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in West Bank-Palestine
- PMID: 31192182
- PMCID: PMC6549579
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2019.00130
Molecular Characterization of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in West Bank-Palestine
Abstract
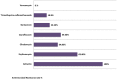
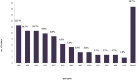
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a public health threat and a major cause of hospital-acquired and community-acquired infections. This study aimed to investigate the genetic diversity of MRSA isolates from 2015 to 2017 and to characterize the major MRSA clones and anti-biogram trends in Palestine. Methodology: Isolates were obtained from 112 patients admitted to different hospitals of West Bank and East Jerusalem, originating from different clinical sources. Antibiotic susceptibility patterns, staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec (SCCmec) typing, and Staphylococcus aureus protein A (spa) typing were determined. Also, a panel of toxin genes and virulence factors was studied, including: Panton-Valentine Leukocidin (PVL), ACME-arcA, Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1), and Exfoliative Toxin A (ETA). Results: Of the 112 confirmed MRSA isolates, 100% were resistant to all β-lactam antibiotics. Resistance rates to other non- β-lactam classes were as the following: 18.8% were resistant to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, 23.2% were resistant to gentamicin, 34.8% to clindamycin, 39.3% to ciprofloxacin, and 63.4% to erythromycin. All MRSA isolates were susceptible to vancomycin (100%). Of all isolates, 32 isolates (28.6%) were multidrug- resistant (MDR). The majority of the isolates were identified as SCCmec type IV (86.6%). The molecular typing identified 29 spa types representing 12 MLST-clonal complexes (CC). The most prevalent spa types were: spa type t386 (CC1)/(12.5%), spa type t044 (CC80)/(10.7%), spa type t008 (CC8)/(10.7%), and spa type t223 (CC22)/(9.8%). PVL toxin gene was detected in (29.5%) of all isolates, while ACME-arcA gene was present in 18.8% of all isolates and 23.2% had the TSST-1 gene. The two most common spa types among the TSST-1positive isolates were the spa type t223 (CC22)/(Gaza clone) and the spa type t021 (CC30)/(South West Pacific clone). All isolates with the spa type t991 were ETA positive (5.4%). USA-300 clone (spa type t008, positive for PVL toxin gene and ACME-arcA genes) was found in nine isolates (8.0%). Conclusions: Our results provide insights into the epidemiology of MRSA strains in Palestine. We report a high diversity of MRSA strains among hospitals in Palestine, with frequent SCCmec type IV carriage. The four prominent clones detected were: t386-IV/ CC1, the European clone (t044/CC80), Gaza clone (t223/CC22), and the USA-300 clone (t008/CC8).
Keywords: MRSA; PVL; SCCmec; TSST-1; USA-300clone; arcA; spa.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MRSA clonal complex 22 strains harboring toxic shock syndrome toxin (TSST-1) are endemic in the primary hospital in Gaza, Palestine.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 17;10(3):e0120008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120008. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25781188 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clones Carrying the Panton-Valentine Leukocidin Genes Disseminating in Iranian Hospitals.Microb Drug Resist. 2018 Dec;24(10):1543-1551. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2018.0033. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Microb Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 29894277
-
Genotyping of community-associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) in a tertiary care centre in Mysore, South India: ST2371-SCCmec IV emerges as the major clone.Infect Genet Evol. 2015 Aug;34:230-5. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.05.032. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Infect Genet Evol. 2015. PMID: 26044198
-
A 6-Year Update on the Diversity of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clones in Africa: A Systematic Review.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 3;13:860436. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.860436. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35591993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution of the Most Prevalent Spa Types among Clinical Isolates of Methicillin-Resistant and -Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus around the World: A Review.Front Microbiol. 2018 Feb 12;9:163. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00163. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29487578 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates in a Tertiary Care Hospital, Kingdom of Bahrain.Cureus. 2023 Apr 7;15(4):e37255. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37255. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37168202 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of mecA and Panton-Valentine Leukocidin Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates from Gaza Strip Hospitals.Microorganisms. 2023 Apr 28;11(5):1155. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051155. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317129 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant and Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Implicated in Bloodstream Infections, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: A Pilot Study.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;13(9):796. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13090796. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334971 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of different virulent factors in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates recovered from Iraqis and Syrian refugees in Duhok city, Iraq.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 17;15(8):e0237714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237714. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32804961 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiology, genetic diversity and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from chicken and pig carcasses, and carcass handlers.PLoS One. 2020 May 14;15(5):e0232913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232913. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32407414 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

