TNFR1 and TNFR2 in the Control of the Life and Death Balance of Macrophages
- PMID: 31192209
- PMCID: PMC6548990
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00091
TNFR1 and TNFR2 in the Control of the Life and Death Balance of Macrophages
Abstract
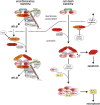
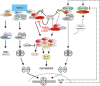
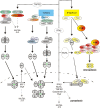
Macrophages stand in the first line of defense against a variety of pathogens but are also involved in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis. To fulfill their functions macrophages sense a broad range of pathogen- and damage-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs/DAMPs) by plasma membrane and intracellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Intriguingly, the overwhelming majority of PPRs trigger the production of the pleiotropic cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF). TNF affects almost any type of cell including macrophages themselves. TNF promotes the inflammatory activity of macrophages but also controls macrophage survival and death. TNF exerts its activities by stimulation of two different types of receptors, TNF receptor-1 (TNFR1) and TNFR2, which are both expressed by macrophages. The two TNF receptor types trigger distinct and common signaling pathways that can work in an interconnected manner. Based on a brief general description of major TNF receptor-associated signaling pathways, we focus in this review on research of recent years that revealed insights into the molecular mechanisms how the TNFR1-TNFR2 signaling network controls the life and death balance of macrophages. In particular, we discuss how the TNFR1-TNFR2 signaling network is integrated into PRR signaling.
Keywords: TNF; TNFR1; TNFR2; apoptosis; caspase-8; necroptosis; ripk1; ripk3.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TNFR2 unlocks a RIPK1 kinase activity-dependent mode of proinflammatory TNFR1 signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 11;9(9):921. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0973-3. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30206205 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of TNFR2 sensitizes macrophages for TNFR1-mediated necroptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Sep 22;7(9):e2375. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.285. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27899821 Free PMC article.
-
Fn14 and TNFR2 as regulators of cytotoxic TNFR1 signaling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 6;11:1267837. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1267837. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38020877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-κB, MAP kinases and cell death.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26993379 Review.
-
Generation of mouse macrophages expressing membrane-bound TNF variants with selectivity for TNFR1 or TNFR2.Cytokine. 2010 Apr;50(1):75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2009.11.022. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Cytokine. 2010. PMID: 20045350
Cited by
-
Novel Biomarkers for Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infection from Synovial Fluid and Serum.JB JS Open Access. 2021 Apr 20;6(2):e20.00067. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.20.00067. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. JB JS Open Access. 2021. PMID: 34056503 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α sculpts a maturation process in vivo by pruning tolerogenic dendritic cells.Cell Rep. 2022 Apr 12;39(2):110657. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110657. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35417681 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages immunomodulation induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis and oral antimicrobial peptides.Odontology. 2023 Oct;111(4):778-792. doi: 10.1007/s10266-023-00798-w. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Odontology. 2023. PMID: 36897441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of Severity and Disease Duration on TNF Receptors' Redistribution in Asthma and Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cells. 2022 Dec 20;12(1):5. doi: 10.3390/cells12010005. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611799 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanistic Pathways Targeted by Natural Antioxidants in the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 22;11(1):15. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010015. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balcewicz-Sablinska M. K., Keane J., Kornfeld H., Remold H. G. (1998). Pathogenic Mycobacterium tuberculosis evades apoptosis of host macrophages by release of TNF-R2, resulting in inactivation of TNF-alpha. J. Immunol. 161 2636–2641. - PubMed
-
- Basu S., Pathak S. K., Banerjee A., Pathak S., Bhattacharyya A., Yang Z., et al. (2007). Execution of macrophage apoptosis by PE_PGRS33 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by Toll-like receptor 2-dependent release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 282 1039–1050. 10.1074/jbc.M604379200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

