Analysis of Plasma EBV-DNA and Soluble Checkpoint Proteins in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients after Definitive Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy
- PMID: 31192256
- PMCID: PMC6525834
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3939720
Analysis of Plasma EBV-DNA and Soluble Checkpoint Proteins in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients after Definitive Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: Tumor immunotherapy and immunological checkpoint-related proteins are research hotspots. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) is the main treatment for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Hence, the evaluation of its effect is very important. The aim of this study was to assess the relationship between the concentrations of soluble checkpoint proteins, plasma EBV-DNA, and cytokines in NPC patients treated with IMRT.
Methods: In this study, the plasma samples of 37 NPC patients and 40 healthy controls were collected. Luminex MAGPIX was used to detect the concentrations of 32 plasma targets, including soluble programmed cell death 1 (sPD-1). RT-qPCR was used to measure EBV-DNA.
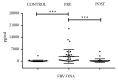
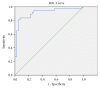
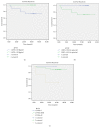
Results: The concentrations of 33 plasma targets were detected in NPC patients before and after IMRT to explore the changes after IMRT. The results showed that IMRT could increase the expression of sPD-1 and significantly reduce the level of EBV-DNA in the plasma of NPC patients. The expression level of sPD-1 in TNM I/II patients was significantly higher than that in III/IV patients. Besides, the concentrations of 12 other targets were significantly different after IMRT, including LAG-3, PD-L1, TIM-3, IFN-γ, IL-12p70, IL-1β, IL-5, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-10, IL-17A, and IL-22. High sPD-1 patients had longer survival than those with low sPD-1. Also, patients with lower EBV-DNA and TNM grades I and II/III had longer survival than those with higher EBV-DNA or TNM IV.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that the concentration of sPD-1 was significantly increased and EBV-DNA was significantly reduced in the NPC patients after IMRT. Plasma EBV-DNA level was a highly specific and sensitive biomarker for NPC diagnosis. Both sPD-1 expression and EBV-DNA concentration in plasma were related to the survival of patients.
Figures

References
-
- Chan A. T., Hui E. P., Ngan R. K., et al. Analysis of plasma epstein-barr virus dna in nasopharyngeal cancer after chemoradiation to identify high-risk patients for adjuvant chemotherapy: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2018;36(31):3091–3100. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.7847. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

