Ascorbate modulates the hypoxic pathway by increasing intracellular activity of the HIF hydroxylases in renal cell carcinoma cells
- PMID: 31192266
- PMCID: PMC6527796
- DOI: 10.2147/HP.S201643
Ascorbate modulates the hypoxic pathway by increasing intracellular activity of the HIF hydroxylases in renal cell carcinoma cells
Abstract
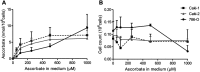
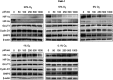
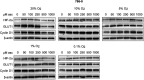
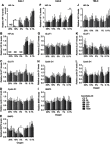
Purpose: Protein levels and activity of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factors HIF-1 and HIF-2 are controlled by hydroxylation of the regulatory alpha chains. Proline hydroxylases (PHDs) target the protein for degradation via the von-Hippel-Lindau (VHL)-ubiquitin-ligase complex, and asparagine hydroxylation by Factor Inhibiting HIF (FIH) leads to transcriptional inactivation. In cell-free systems, these enzymes require ascorbate as a cofactor, and this is also inferred to be an intracellular requirement for effective hydroxylation. However, how intracellular concentrations of ascorbate affect hydroxylase activity is unknown. In this study, we investigated the modulation of the regulatory hydroxylases in cancer cells by intracellular ascorbate. Materials and methods: To facilitate this investigation, we used clear cell renal carcinoma cell lines that were VHL-proficient (Caki-1), with a normal hypoxic response, or VHL-defective (Caki-2 and 786-0), with uncontrolled accumulation of HIF-α chains. We monitored the effect of intracellular ascorbate on the hypoxia-induced accumulation of HIF-1α, HIF-2α and the expression of downstream HIF targets BNIP3, cyclin D1 and GLUT1. Changes in hydroxylation of the HIF-1α protein in response to ascorbate were also investigated in 786-0 cells gene-modified to express full-length HIF-1α (786-HIF1). Results: In VHL-proficient cells, hypoxia induced accumulation of HIF-1α and BNIP3 which was dampened in mild hypoxia by elevated intracellular ascorbate. Increased HIF-2α accumulation occurred only under severe hypoxia and this was not modified by ascorbate availability. In VHL-defective cells, ascorbate supplementation induced additional accumulation of HIF under hypoxic conditions and HIF pathway proteins were unchanged by oxygen supply. In 786-HIF1 cells, levels of hydroxylated HIF-1α were elevated in response to increasing intracellular ascorbate levels. Conclusion: Our data provide evidence that the hypoxic pathway can be modulated by increasing HIF hydroxylase activity via intracellular ascorbate availability. In VHL-defective cells, accumulation of HIF-alpha proteins is independent of hydroxylation and is unaffected by intracellular ascorbate levels.
Keywords: PHD; VHL; ccRCC; hypoxia inducible factor-1; kidney cancer; vitamin C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Association Between Ascorbate and the Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Human Renal Cell Carcinoma Requires a Functional Von Hippel-Lindau Protein.Front Oncol. 2018 Nov 30;8:574. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00574. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30555801 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Hydroxylation by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) Hydroxylases: Unique or Ubiquitous?Cells. 2019 Apr 26;8(5):384. doi: 10.3390/cells8050384. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31035491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha under normoxic conditions in renal carcinoma cells by von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene loss of function.Oncogene. 2000 Nov 16;19(48):5435-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203938. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11114720
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) promotes its degradation by induction of HIF-alpha-prolyl-4-hydroxylases.Biochem J. 2004 Aug 1;381(Pt 3):761-7. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040620. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15104534 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) pathway.Sci STKE. 2007 Oct 9;2007(407):cm8. doi: 10.1126/stke.4072007cm8. Sci STKE. 2007. PMID: 17925579 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Ascorbate Requirement of the 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases.J Med Chem. 2025 Feb 13;68(3):2219-2237. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02342. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39883951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Sodium-Dependent Vitamin C Transporter-2 and Ascorbate in Regulating the Hypoxic Pathway in Cultured Glioblastoma Cells.J Cell Biochem. 2025 Jan;126(1):e30658. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30658. Epub 2024 Oct 9. J Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39382087 Free PMC article.
-
Yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional coactivator with a PDZ-binding motif (TAZ): a nexus between hypoxia and cancer.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Jun;10(6):947-960. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.12.010. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 32642404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Oxygen Homeostasis and the HIF-1 Factor in the Development of Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 23;25(9):4581. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094581. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G6PD deficiency, redox homeostasis, and viral infections: implications for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19).Free Radic Res. 2021 Apr;55(4):364-374. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2020.1866757. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Free Radic Res. 2021. PMID: 33401987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

