Effects of surgery start time on postoperative cortisol, inflammatory cytokines, and postoperative hospital day in hip surgery: Randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 31192911
- PMCID: PMC6587638
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015820
Effects of surgery start time on postoperative cortisol, inflammatory cytokines, and postoperative hospital day in hip surgery: Randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare morning surgery (Group A), characterized by high cortisol levels, with afternoon surgery (Group B), characterized by low cortisol levels, with respect to cortisol, inflammatory cytokines (interleukin [IL]-6, IL-8), and postoperative hospital days (POHD) after hip surgery.
Methods: The study was conducted in a single center, prospective, randomized (1:1) parallel group trial. Patients undergoing total hip replacement or hemiarthroplasty were randomly divided into two groups according to the surgery start time: 8 AM (Group A) or 1-2 PM (Group B). Cortisol and cytokine levels were measured at 7:30 AM on the day of surgery, before induction of anesthesia, and at 6, 12, 24, and 48 hours (h) after surgery. Visual analogue scale (VAS) and POHD were used to evaluate the clinical effect of surgery start time. VAS was measured at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h postoperatively, and POHD was measured at discharge.
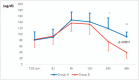
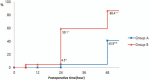
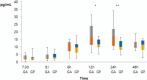
Results: In total, 44 patients completed the trial. The postoperative cortisol level was significantly different between the two groups. (24 h, P < .001; 48 h, P < .001). The percentage of patients whose level returned to the initial level was higher in Group B than in Group A (P < .001). Significant differences in IL-6 levels were observed between the two groups at 12, 24, and 48 h after surgery (P = .015; P = .005; P = .002), and in IL-8 levels at 12 and 24 h after surgery (P = .002, P < .001). There was no significant difference between the two groups in VAS and POHD. However, only three patients in Group A were inpatients for more than 3 weeks (P = .233).
Conclusions: Afternoon surgery allowed for more rapid recovery of cortisol to the baseline level than morning surgery, and IL-6 and IL-8 were lower at 1-2 days postoperatively. The results of this study suggest that afternoon surgery may be considered in patients with postoperative delayed wound healing or inflammation because of the difference in cortisol, IL-6 and 8 in according to surgery start time.
Clinical trial registration number: NCT03076827 (ClinicalTRrial.gov).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of cortisol and inflammatory response between aged and middle-aged patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty: a prospective observational study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Dec 19;18(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1900-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 29258488 Free PMC article.
-
[The effects of general anesthesia combined with epidural anesthesia on the stress response in thoracic surgery].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003 Mar 10;83(5):408-11. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 12820919 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
The effects of morning/afternoon surgeries on the early postoperative sleep quality of patients undergoing general anesthesia.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Sep 10;22(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01828-w. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 36088298 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated plasma levels of interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor during and after major abdominal surgery.J Clin Anesth. 1997 Jun;9(4):293-8. doi: 10.1016/s0952-8180(97)00006-8. J Clin Anesth. 1997. PMID: 9195352 Clinical Trial.
-
Inflammatory cytokines in relation to adrenal response following total hip replacement.Scand J Immunol. 2007 Jan;65(1):99-105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2006.01872.x. Scand J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17212773
Cited by
-
Effect of low-pressure pneumoperitoneum on pain and inflammation in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled clinical trial.BMC Res Notes. 2023 Sep 28;16(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s13104-023-06492-y. BMC Res Notes. 2023. PMID: 37770908 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The timing of the mouse hind paw incision does not influence postsurgical pain.Neurobiol Pain. 2024 Aug 2;16:100161. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2024.100161. eCollection 2024 Jul-Dec. Neurobiol Pain. 2024. PMID: 39188910 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative Delirium in Neurosurgical Patients: Recent Insights into the Pathogenesis.Brain Sci. 2022 Oct 9;12(10):1371. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12101371. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36291305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular biology of periodontal ligament fibroblasts and orthodontic tooth movement : Evidence and possible role of the circadian rhythm.J Orofac Orthop. 2019 Nov;80(6):336-347. doi: 10.1007/s00056-019-00195-5. Epub 2019 Sep 18. J Orofac Orthop. 2019. PMID: 31650205 English.
-
Major surgery leads to a proinflammatory phenotype: Differential gene expression following a laparotomy.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021 Oct 21;71:102970. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102970. eCollection 2021 Nov. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34745602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AC G, JE H. Medical Physiology. 11th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders; 2006.
-
- Hogevold HE, Lyberg T, Kahler H, et al. Changes in plasma IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and IL-6 after total hip replacement surgery in general or regional anesthesia. Cytokine 2000;12:1156–9. - PubMed
-
- Crozier TA, Muller JE, Quittkat D, et al. Effect of anesthesia on the cytokine responses to abdominal surgery. Brit J Anesth 1994;72:280–5. - PubMed
-
- Ram E, Vishne TH, Weinstein T, et al. General anesthesia for surgery influences melatonin and cortisol levels. World J Surg 2005;29:826–9. - PubMed
-
- Naito Y, Tamai S, Shingu K, et al. Responses of plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol, and cytokines during and after upper abdominal surgery. Anesthesiology 1992;77:426–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

