Effectiveness of Chinese herbal medicine for patients with primary insomnia: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis
- PMID: 31192935
- PMCID: PMC6587651
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015967
Effectiveness of Chinese herbal medicine for patients with primary insomnia: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Traditional medicine is widely used for patients with primary insomnia, but the studies showed inconsistent results. We performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to evaluate the effectiveness of Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) versus placebo for primary insomnia patients.
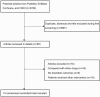
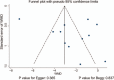
Methods: The electronic databases including PubMed, EmBase, Cochrane library, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure were searched to identify the RCTs published from inception till July 2018. The summary weighted mean difference (WMD) with its 95% confidence interval (CI) for Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI), sleep onset latency, total sleep duration, Athens insomnia scale (AIS), and sleep efficiency were calculated using random-effects model.
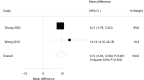
Results: Fifteen RCTs comprising 1500 patients were finally included in the meta-analysis. Overall, patients who received CHM had lower levels of PSQI (WMD: -2.36; 95% CI: -4.02 to -0.70; P = .005), sleep onset latency (WMD: -11.54; 95% CI: -20.55 to -2.54; P = .012), and AIS (WMD: -0.59; 95% CI: -0.97 to -0.22; P = .002) as compared with placebo. Moreover, the summary WMDs of CHM versus placebo were associated with higher total sleep duration (WMD: 0.79; 95% CI: 0.56-1.02; P < .001), and sleep efficiency (WMD: 9.72; 95% CI: 6.49-12.96; P < .001). The treatment effect on PSQI might be affected by publication year, sample size, mean age, percentage male, diagnostic tool, duration of insomnia, treatment duration, and study quality.
Conclusion: The findings of this meta-analysis indicated that CHM could significantly improve the symptoms of insomnia than placebo for patients with primary insomnia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chinese herbal medicine and acupuncture for insomnia in stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Sleep Med. 2024 Aug;120:65-84. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2024.05.006. Epub 2024 May 11. Sleep Med. 2024. PMID: 38905930
-
Meta analysis for insomnia Guizhi Gancao Longgu Muli decoction for insomnia A meta-analysis.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2022 May;47:101550. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2022.101550. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 35235882 Review.
-
Zao Ren An Shen for insomnia: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Sleep Med. 2020 May;69:41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2019.12.023. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Sleep Med. 2020. PMID: 32045853
-
Efficacy and safety of Wuling capsule for insomnia disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Sleep Med. 2022 May;93:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2022.03.014. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Sleep Med. 2022. PMID: 35397258
-
Wendan decoction for primary insomnia: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Nov;96(47):e8906. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008906. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29382025 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Herbal Medicine on Suicidal Behavior: A Protocol for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 May 11;11(10):1387. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11101387. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239673 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of insomnia based on the mechanism of pathophysiology by acupuncture combined with herbal medicine: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Mar 17;102(11):e33213. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033213. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36930068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Symptom Distribution Regularity of Insomnia: Network and Spectral Clustering Analysis.JMIR Med Inform. 2020 Apr 16;8(4):e16749. doi: 10.2196/16749. JMIR Med Inform. 2020. PMID: 32297869 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicine for post-stroke insomnia: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jun 4;100(22):e26223. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026223. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34087901 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional East Asian Herbal Medicine for Post-Stroke Insomnia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 3;19(3):1754. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19031754. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35162777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Edinger JD, Bonnet MH, Bootzin RR, et al. Derivation of research diagnostic criteria for insomnia: report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Work Group. Sleep 2004;27:1567–96. - PubMed
-
- Trauer JM, Qian MY, Doyle JS, et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy for chronic insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2015;163:191–204. - PubMed
-
- Morin CM, LeBlanc M, Daley M, et al. Epidemiology of insomnia: prevalence, self-help treatments, consultations, and determinants of help-seeking behaviors. Sleep Med 2006;7:123–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

