Knockdown of TRAF3IP2 suppresses the expression of VEGFA and the proliferation of keratinocytes and vascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 31193034
- PMCID: PMC6513784
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01642
Knockdown of TRAF3IP2 suppresses the expression of VEGFA and the proliferation of keratinocytes and vascular endothelial cells
Abstract
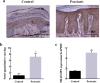
Objective: To investigate the expression level of TRAF3IP2 in psoriasis lesion, and to explore the functional roles of TRAF3IP2 on proliferation, apoptosis, cytokine expression and secretion of both keratinocytes and vascular endothelial cells in vitro.
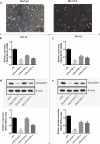
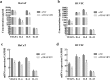
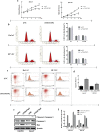
Methods: The expression of TRAF3IP2 in skin samples of patients with psoriasis was analyzed by immunohistochemistry and qRT-PCR. To identify the effect of TRAF3IP2 knockdown on HaCaT and HUVEC cells, a plasmid vector expressing siRNA targeting TRAF3IP2 mRNA was designed and transfected into cells with Lipofectamine 2000. The levels of cytokines were identified using the ELISA Kits and qRT-PCR. Furthermore, cell proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis were examined by using MTT, PI and Annexin V-FITC/7AAD assays, respectively. Furthermore, the expression of apoptosis-related proteins (Cleaved-Caspase 3, Caspase 3 and Bax) were detected by western blotting.
Results: TRAF3IP2 was significantly upregulated in psoriasis lesion. TRAF3IP2 knockdown reduced the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and the release of IL-6, and IL-8, but had no effect on IL-23 in both HaCaT and HUVEC cells. In addition, knockdown of TRAF3IP2 significantly inhibited cell proliferation through blocking the cell cycle in the G2/M phase. Moreover, knockdown of TRAF3IP2 increased the expression of Caspase 3, Cleaved-Caspase 3 and Bax, which was supported by the increased apoptosis of both HaCaT and HUVEC cells.
Conclusion: Taken together, these results indicated that TRAF3IP2 might play a contributive role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and may serve as a new target for the treatment of psoriasis. VEGF related pathways may be involved in the mechanism beneath.
Keywords: Cell biology; Genetics; Molecular biology; Physiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-17 promotes proliferation, inflammation and inhibits apoptosis of HaCaT cells via interacting with the TRAF3 interacting protein 2.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jan;21(1):49. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9480. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33273977 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1 regulates the proliferation, apoptosis and inflammatory response of keratinocytes through the NF-κB signaling pathway.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021 Jul;40(7):1130-1140. doi: 10.1177/0960327120984225. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33401961
-
MiR-149-5p inhibits cell proliferation, promotes cell apoptosis and retards cell cycle of IL-22-stimulated HaCaT and NHEK keratinocytes via regulating PDE4D.Cytokine. 2023 Apr;164:156123. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156123. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Cytokine. 2023. PMID: 36796259
-
MiR-126 correlates with increased disease severity and promotes keratinocytes proliferation and inflammation while suppresses cells' apoptosis in psoriasis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2018 Nov;32(9):e22588. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22588. Epub 2018 Jun 26. J Clin Lab Anal. 2018. PMID: 29943471 Free PMC article.
-
18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid induces human HaCaT keratinocytes apoptosis through ROS-mediated PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and ameliorates IMQ-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020 Jun 3;21(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s40360-020-00419-0. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32493482 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A VEGFA Inhibition: An Effective Treatment Strategy for Psoriasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 20;25(1):59. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010059. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAF3IP2 drives mesenchymal stem cell senescence via regulation of NAMPT-mediated NAD biosynthesis.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 29;9(9):e19505. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19505. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809895 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted siRNA Therapy for Psoriasis: Translating Preclinical Potential into Clinical Treatments.Immunotargets Ther. 2024 May 16;13:259-271. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S458800. eCollection 2024. Immunotargets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38770264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fernandez-Armenteros J.M., Gomez-Arbones X., Buti-Soler M., Betriu-Bars A., Sanmartin-Novell V., Ortega-Bravo M. Psoriasis, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk factors. A population-based study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

