Sex differences in cardiac and renal responses to a high salt diet in Sprague-Dawley rats
- PMID: 31193051
- PMCID: PMC6514751
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01665
Sex differences in cardiac and renal responses to a high salt diet in Sprague-Dawley rats
Abstract
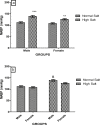
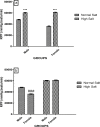
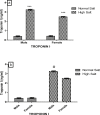
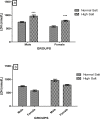
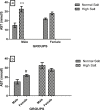
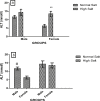
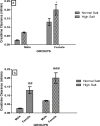
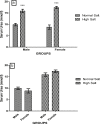
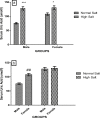
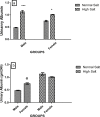
High dietary salt intake is an important risk factor for cardiovascular and renal diseases. However, sexual disparity exists in the response of target organs to high salt diet (HSD). To determine how sex affects cardiac and renal functions' response to HSD, 20 weanling Sprague-Dawley rats (10 males and 10 females) were divided into 4 groups of 5 rats each. The rats were fed a normal diet (0.3% NaCl) or HSD (8% NaCl) for 12 weeks. Fluid balance (FB) was determined from 24 hrs water intake and voided urine. Blood pressure (BP) was measured via arterial cannulation under anesthesia (25% w/v urethane and 1% w/v α-chloralose; 5 ml/kg, i.p). Serum levels of troponin I, aminotransaminases, creatinine, urea, uric acid and electrolytes as well as urinary concentration of albumin, creatinine, and electrolytes were measured using appropriate assay kits. Values are presented as mean ± S.E.M, compared by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post Hoc test. In the male rat, HSD significantly increased BP, serum: Troponin I, LDH and sodium (p < 0.05), urinary: albumin, sodium, potassium and FB (p < 0.05). In the female rat, HSD increased BP, serum: troponin I, LDH, sodium and creatinine clearance (p < 0.05), urinary: albumin, sodium and potassium (p < 0.01). However, HSD increased more, the BP, serum: Troponin I, LDH, urinary albumin and FB in male rats, while HSD increased urinary sodium more in female rats. Basal values in male vs. female of serum LDH and urinary albumin were significantly different. Thus, sex plays an important role in the response of the heart and kidney to salt stress.
Keywords: Pathology; Physiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Orchidectomy attenuates high-salt diet-induced increases in blood pressure, renovascular resistance, and hind limb vascular dysfunction: role of testosterone.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Sep;43(9):825-33. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12595. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27197589
-
Angiotensin II Type 2-Receptor Agonist C21 Reduces Proteinuria and Oxidative Stress in Kidney of High-Salt-Fed Obese Zucker Rats.Hypertension. 2016 May;67(5):906-15. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06881. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27021008 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin mediates sex-differences in acclimation to high salt diet in rats.Biol Sex Differ. 2023 Oct 10;14(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00555-2. Biol Sex Differ. 2023. PMID: 37817272 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterization of the "new" Harlan Sprague Dawley Dahl salt-sensitive rats.Hypertension. 1996 Mar;27(3 Pt 2):546-51. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.27.3.546. Hypertension. 1996. PMID: 8613201
-
Association of Antihypertensive Effects of Esaxerenone with the Internal Sodium Balance in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Hypertensive Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 10;23(16):8915. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168915. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012182 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Phyllanthus amarus attenuated derangement in renal-cardiac function, redox status, lipid profile and reduced TNF-α, interleukins-2, 6 and 8 in high salt diet fed rats.Heliyon. 2021 Oct 1;7(10):e08106. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08106. eCollection 2021 Oct. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34660924 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen sulfide alleviates high-salt-stimulated myocardial fibrosis through inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1502269. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1502269. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40642013 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Doenjang, a Traditional Korean Soybean Paste, with High-Salt Diet on Blood Pressure in Sprague-Dawley Rats.Nutrients. 2019 Nov 12;11(11):2745. doi: 10.3390/nu11112745. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31726743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D’Elia L., Galletti F., La Fata E., Sabino P., Strazzullo P. Effect of dietary sodium restriction on arterial stiffness: systematic review and meta-analysis of the randomized controlled trials. J. Hypertens. 2018;36(4):734–743. - PubMed
-
- Meneton P., Jeunemaitre X., de Wardener H.E., Macgregor G.A. Links between dietary salt intake, renal salt handling, blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2005;85(2):679–715. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger M.H., Fineberg N.S., Fineberg S.E., Weinberger M. Salt sensitivity, pulse pressure, and death in normal and hypertensive humans. Hypertension. 2001;37(2):429–432. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

