IL-7R blockade reduces post-myocardial infarction-induced atherosclerotic plaque inflammation in ApoE-/- mice
- PMID: 31193072
- PMCID: PMC6517313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2019.100647
IL-7R blockade reduces post-myocardial infarction-induced atherosclerotic plaque inflammation in ApoE-/- mice
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing Declaration of Competing Interest statements in previously published articles.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Jan 7;25:100901. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100901. eCollection 2021 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 33614995 Free PMC article.
Abstract
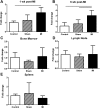
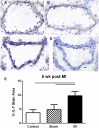
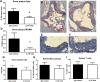
Modulating inflammation by targeting IL-1β reduces recurrent athero-thrombotic cardiovascular events without lipid lowering. This presents an opportunity to explore other pathways associated with the IL-1β signaling cascade to modulate the inflammatory response post-myocardial infarction (MI). IL-7 is a mediator of the inflammatory pathway involved in monocyte trafficking into atherosclerotic plaques and levels of IL-7 have been shown to be elevated in patients with acute MI. Recurrent athero-thrombotic events are believed to be mediated in part by index MI-induced exacerbation of inflammation in atherosclerotic plaques. The objective of the study was to assess the feasibility of IL-7R blockade to modulate atherosclerotic plaque inflammation following acute MI in ApoE-/- mice. Mice were fed Western diet for 12 weeks and then subjected to coronary occlusion to induce an acute MI. IL-7 expression was determined using qRT-PCR and immuno-staining, and IL-7R was assessed using flow cytometry. Plaque inflammation was evaluated using immunohistochemistry. IL-7R blockade was accomplished with monoclonal antibody to IL-7R. IL-7 mRNA expression was significantly increased in the cardiac tissue of mice subjected to MI but not in controls. IL-7 staining was observed in the coronary artery. Plaque macrophage and lipid content were significantly increased after MI. IL-7R antibody treatment but not control IgG significantly reduced macrophage and lipid content in atherosclerotic plaques. The results show that IL-7R antibody treatment reduces monocyte/macrophage and lipid content in the atherosclerotic plaque following MI suggesting a potential new target to mitigate increased plaque inflammation post-MI.
Keywords: IL-7R; Myocardial infarction; Plaque inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Kikkert W.J., Hoebers L.P., Damman P., Lieve K.V., Claessen B.E., Vis M.M., Baan J., Jr., Koch K.T., de Winter R.J., Piek J.J., Tijssen J.G., Henriques J.P. Recurrent myocardial infarction after primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014;113(2):229–235. - PubMed
-
- Remskar M., Horvat M., Hojker S., Noc M. Procalcitonin in patients with acute myocardial infarction Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2002;114(5–6):205–210. - PubMed
-
- Joshi N.V., Toor I., Shah A.S., Carruthers K., Vesey A.T., Alam S.R., Sills A., Hoo T.Y., Melville A.J., Langlands S.P., Jenkins W.S., Uren N.G., Mills N.L., Fletcher A.M., van Beek E.J., Rudd J.H., Fox K.A., Dweck M.R., Newby D.E. Systemic atherosclerotic inflammation following acute myocardial infarction: myocardial infarction begets myocardial infarction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015;4(9):e001956. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ridker P.M., Everett B.M., Thuren T., MacFadyen J.G., Chang W.H., Ballantyne C., Fonseca F., Nicolau J., Koenig W., Anker S.D., Kastelein J.J.P., Cornel J.H., Pais P., Pella D., Genest J., Cifkova R., Lorenzatti A., Forster T., Kobalava Z., Vida-Simiti L., Flather M., Shimokawa H., Ogawa H., Dellborg M., Rossi P.R.F., Troquay R.P.T., Libby P., Glynn R.J. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;377(12):1119–1131. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

