Exploring the potential role of sonic hedgehog cell signalling pathway in antidepressant effects of nicotine in chronic unpredictable mild stress rat model
- PMID: 31193084
- PMCID: PMC6514495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01600
Exploring the potential role of sonic hedgehog cell signalling pathway in antidepressant effects of nicotine in chronic unpredictable mild stress rat model
Abstract
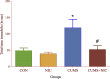
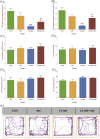
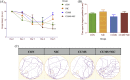
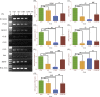
Nicotine is the most common and highly addictive drug of abuse, associated with several life-threatening diseases and high mortality. Nicotine abuse is the concerted effort to feel reward and fight depression in depressed individuals. The underlying mechanism of nicotine is to activate the brain reward system in the central nervous system and provide an antidepressant effect. Antidepressants provide their therapeutic effect by stimulating hippocampal neurogenesis, which can be correlated with brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in the hippocampus. BDNF interacts with Wnt/β-catenin and sonic hedgehog (Shh) signalling cascade to stimulate hippocampal neurogenesis. Shh is the marker of hippocampal neurogenesis and also involved in the neuropathology of depression. But knowledge in this area to identify the potential therapeutic target is limited. In our study, we explored the role of BDNF, Wnt/β-catenin and Shh signalling in depression and the involvement of these signalling pathways in providing an antidepressant effect by nicotine. Our investigations showed that chronic unpredictable mild stress induced depression results declined expression of BDNF, Wnt/β-catenin, Shh and its downstream transcription factors GLI1/2/3 and NKX2.2 in the hippocampus of male Wistar rat. Moreover, we also observed that nicotine administration increased the expression of these signalling molecules in providing the antidepressant effects.
Keywords: Neuroscience.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring Sonic Hedgehog Cell Signaling in Neurogenesis: Its Potential Role in Depressive Behavior.Neurochem Res. 2021 Jul;46(7):1589-1602. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03307-z. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 33786718 Review.
-
Sonic hedgehog, Wnt, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor cell signaling pathway crosstalk: potential therapy for depression.J Neurosci Res. 2018 Jan;96(1):53-62. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24104. Epub 2017 Jun 20. J Neurosci Res. 2018. PMID: 28631844 Review.
-
Andrographolide Exerts Significant Antidepressant-Like Effects Involving the Hippocampal BDNF System in Mice.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019 Sep 1;22(9):585-600. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyz032. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31181145 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of chronic unpredictable mild stress induced prenatal stress on neurodevelopment of neonates: Role of GSK-3β.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 4;9(1):1305. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38085-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30718708 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior: involvement of the HPA axis, inflammatory markers, BDNF, and Wnt/β-catenin pathway in rats.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017 Oct 27;13:2727-2736. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S150028. eCollection 2017. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017. PMID: 29138567 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ablated Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in the Dentate Gyrus of the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus Impairs Hippocampal-Dependent Memory Tasks and Emotion in a Rat Model of Depression.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):4352-4368. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03796-9. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38087166
-
M6A RNA epitranscriptome dynamics linked to major depressive disorder and suicide risk.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025 Sep;50(10):1524-1535. doi: 10.1038/s41386-025-02165-5. Epub 2025 Jul 10. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40640508 Free PMC article.
-
Renin-angiotensin system: The underlying mechanisms and promising therapeutical target for depression and anxiety.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 24;13:1053136. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1053136. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36761172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Sonic Hedgehog Cell Signaling in Neurogenesis: Its Potential Role in Depressive Behavior.Neurochem Res. 2021 Jul;46(7):1589-1602. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03307-z. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 33786718 Review.
-
Smo-Shh Agonist Purmorphamine Prevents Neurobehavioral and Neurochemical Defects in 8-OH-DPAT-Induced Experimental Model of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder.Brain Sci. 2022 Mar 2;12(3):342. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12030342. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35326298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang M., Xu W., He G., Zhang D., Zhao X., Dai J., Wu J., Cao Y., Wang Z., Wang L., Qiao Z. Maternal nicotine exposure has severe cross-generational effects on offspring behavior. Behav. Brain Res. 2018;348:263–266. - PubMed
-
- WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2017. Monitoring Tobacco Use and Prevention Policies. 2017.
-
- W.H. Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2017. Depression and other common mental disorders: global health estimates; p. 24.
-
- Perkins K.A., Grobe J.E. Increased desire to smoke during acute stress. Br. J. Addict. 1992;87:1037–1040. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

